Figure 7.
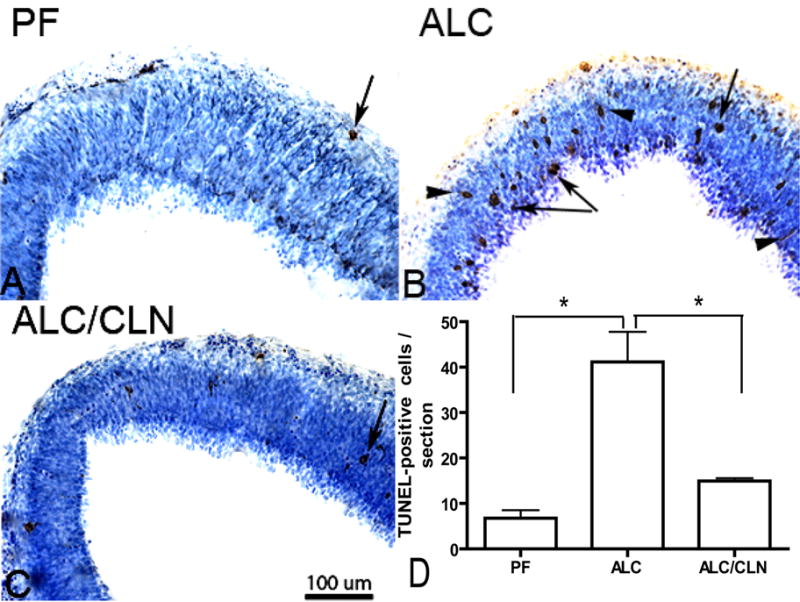
Prenatal alcohol exposure increases the number of TUNEL-positive cells in primordium frontal cortex (A, B, C) of E13 fetal brains. Administration of colivelin (CLN) alongside alcohol exposure prevented alcohol-induced increases in TUNEL-positive cells. Arrowheads indicate cell undergoing apoptosis as indicated by cell processes, and arrows indicate the final stage of cell death. Scale bars: 100 μm. The one-way ANOVA demonstrated a significant difference between groups (p=0.0032). An increase in TUNEL-positive cells was found in the ALC group as compared to the PF group (p<0.01) (D). Importantly, CLN administration alongside alcohol exposure prevented a significant alcohol-induced increase in TUNEL-positive cells (p<0.01) (D). Values are shown as mean ± SEM. (PF, n=5; ALC, n=6; ALC/CLN, n=5). * p<0.01 (Newman-Keul’s post hoc test).
