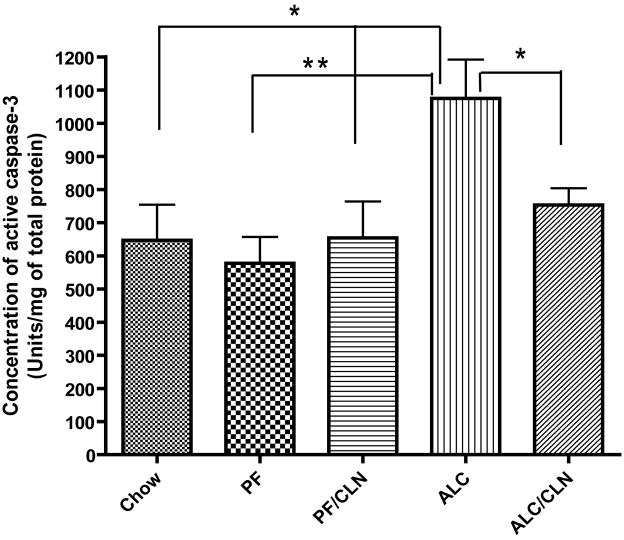
Figure 8.
Neuroprotective effect of colivelin (CLN) against the insult of prenatal alcohol exposure is mediated through caspase-3 activation as tested by caspase-3 colorimetric assay in E13 fetal brains. The one-way ANOVA demonstrated a significant difference between groups (p=0.0039). Prenatal alcohol exposure induced a significant increase in the concentrations of active caspase-3 as compared to the Chow and PF control groups (p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). CLN administration prevented significantly the effect of alcohol-induced increases in the concentrations of active caspase-3 (p<0.05). There were no significant differences between the control and CLN treatment groups. Values are shown as mean ± SEM. (Chow, n=5; PF, n=9; ALC, n=8; ALC/CLN, n=6). * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 (Newman-Keul’s post hoc test).