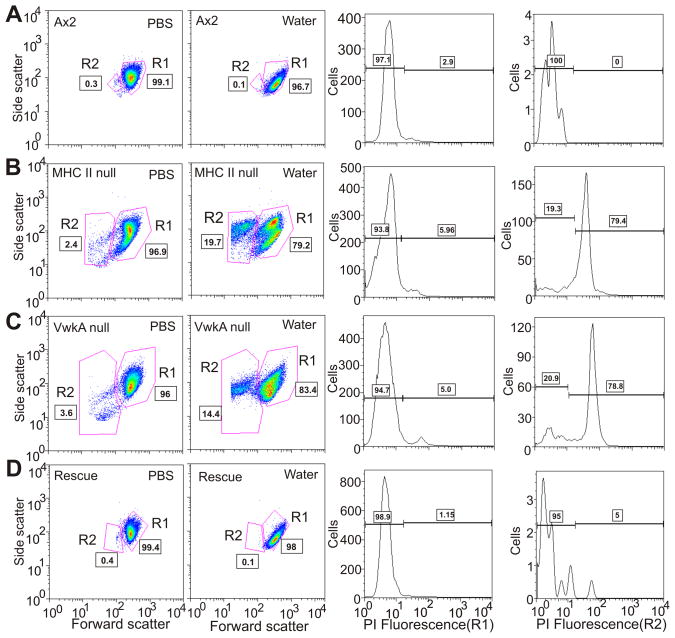
Figure 4. VwkA protects cells from cell death induced by hypo-osmotic shock.
Indicated cell types, attached to plastic petri dishes, were switched from HL5 medium to either PBS or water for 60 minutes, then collected for viability analysis based up flow cytometry-based light scattering properties and propidium iodide (PI) staining, using recently described methods (39). Identified based on light scattering properties, the R1 population represents healthy cells and the R2 population is enriched in dying cells. The left two columns indicate the water-induced increase in the R2 population observed in mhcA− cells (B) and vwkA− cells (C), which is not observed in either parental Ax2 (A) nor in vwkA− cells rescued with a full-length plasmid-based VwkA cDNA (D). The right two column report PI staining for each water-treated set of cells, scored either in the R1 population (third column from left) or in the R2 population (last column on right). This PI analysis reveals a strong increase in PI-staining dead cells in the mhcA− population (B), and in the vwkA− population (C), which is not observed in either parental Ax2 (A) nor in vwkA− cells rescued with a full-length plasmid-based VwkA cDNA (D).