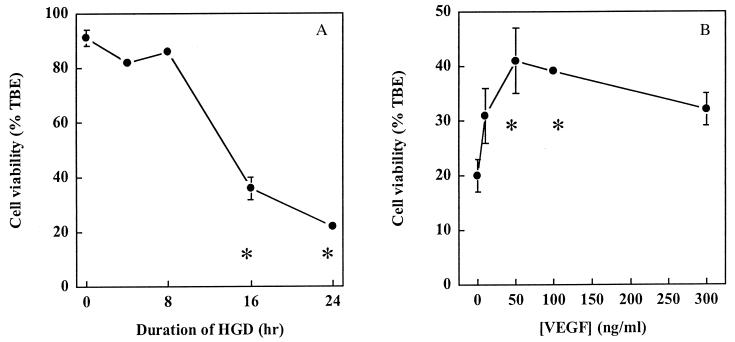
Figure 1.
Protection of HN33 cells from hypoxia and glucose deprivation (HGD) by VEGF. (A) Cultures were maintained in oxygen- and glucose-free medium for the indicated times, and cell viability at 24 h was determined by counting cells excluding trypan blue dye (TBE) as a percentage of all cells. Cell viability after 16 and 24 h of HGD was significantly different from that at 0 h (P < 0.05 by ANOVA and Student–Newman–Keuls tests). (B) VEGF was added to cultures at the indicated concentrations at the onset of exposure to HGD for 24 h. Data shown in A and B are mean values ± SEM from representative experiments, performed in triplicate, which were repeated three times with similar results. Asterisks indicate P < 0.05 by ANOVA and Student—Newman–Keuls tests relative to 0 h of HGD (A) or 0 ng/ml of VEGF (B).