Table 2. Prediction and testing of new cross-boundary targets for drugs.
| Drug / Canonical Target | E-value | Predicted Target | Ki (nM)‡ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
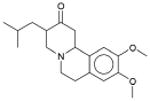 |
Xenazine VMAT2 (transporter) |
1.4×10-61 | α2 Adrenergic receptor † (GPCR) | α2A | 960 |
| α2C | 1.3×103 | ||||
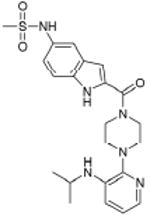 |
Rescriptor HIV-1 RT (enzyme) |
1.05×10-30 | Histamine H4 receptor (GPCR) | 5.3×103 | |
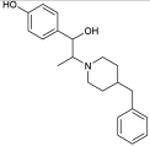 |
Vadilex NMDAR (ion channel) |
5.14×10-13 | μ Opioid receptor (GPCR) | 1.4×103 | |
| 1.98×10-4 | 5-HTT; Serotonin transporter (transporter) | 77 | |||
 |
RO-25-6981 NMDAR (ion channel) |
1.53×10-8 | 5-HTT; Serotonin transporter (transporter) | 1.4×103 | |
| 1.94×10-6 | Dopamine D4 receptor (GPCR) | 120 | |||
| 3.61×10-6 | NET; Norepinephrine transporter (transporter) | 1.3×103 | |||
| 9.08×10-5 | κ Opioid receptor (GPCR) | 3.1×103 | |||
The MDDR database did not specify the α2 adrenergic receptor subtype, requiring a separate assay for each one (α2A, α2C).
Ki values are accurate ± 20% at two significant figures.
