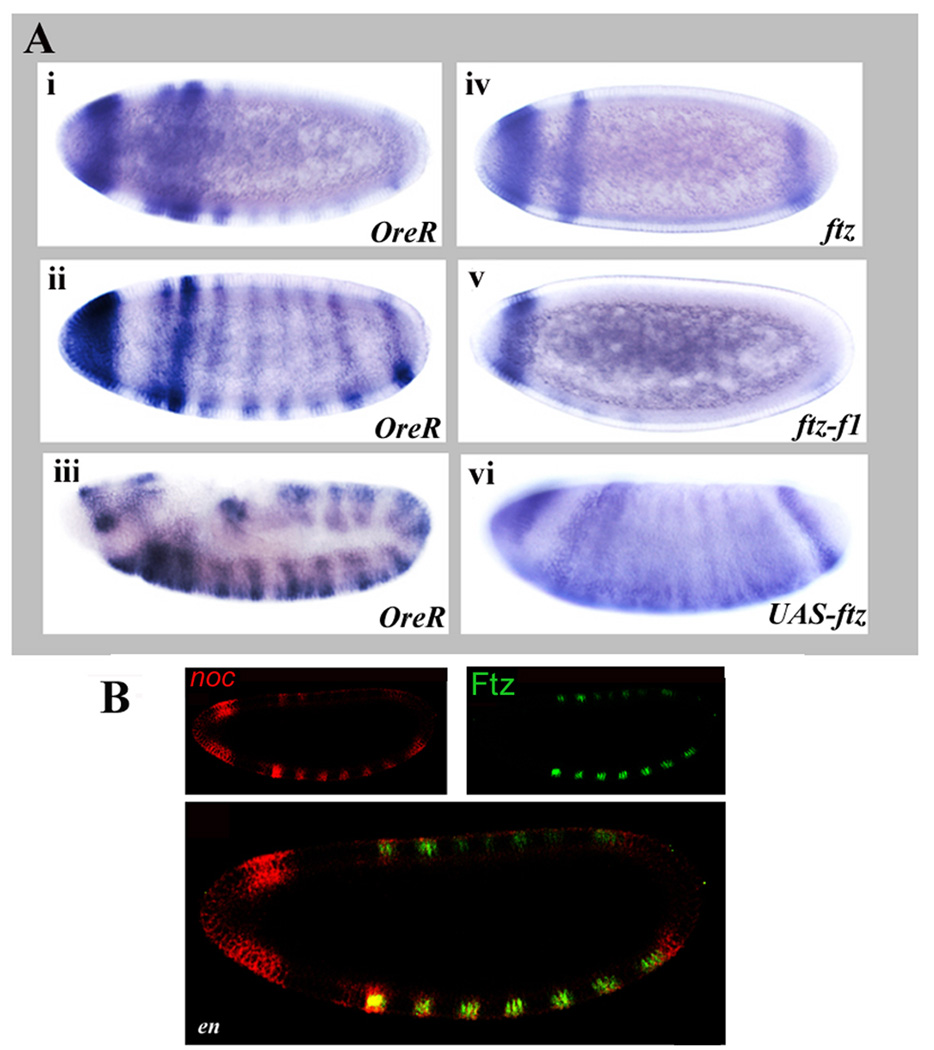
Figure 2. ftz and ftz-f1 regulate noc expression.
(A) noc expression is dependent upon ftz and ftz-f1. In situ hybridization of noc mRNA: (i,ii,iii) OreR, at cellular blastoderm and late germ band extension stages show early expression in the head and in eight stripes, developing into a 14 stripe pattern; (iv) ftz9H34 mutant embryo; (v) ftz-f1ex19 mutant embryo; and (vi) UAS-myc-ftz/NGT40 embryo. In ftz mutant embryos, the six central noc stripes are missing while ectopic Ftz induced ectopic noc expression. (B) Ftz regulates noc expression independent of en. Confocal images of embryos stained for noc mRNA (red) or Ftz protein, as indicated, in an en1 mutant embryo: noc RNA (red), Ftz protein (green). Note that Ftz protein is nuclear and noc RNA is cytoplasmic, so cellular colocalization does not produce a yellow color. No change was observed in the noc expression pattern in en mutants, as compared to wild type controls.