Figure 1.
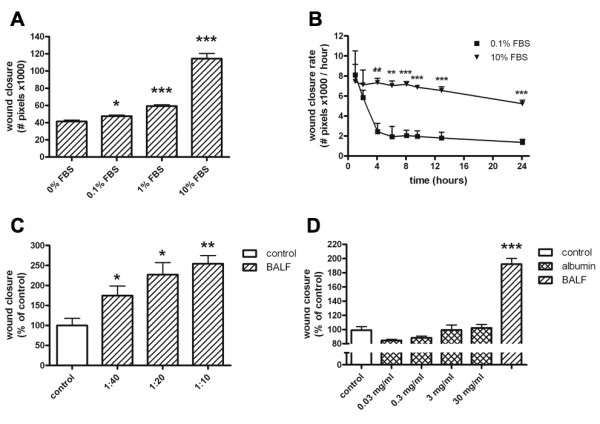
Characterisation of the alveolar epithelial wound repair model. A. Effect of addition of various concentrations of fetal bovine serum (FBS) to culture medium on in vitro alveolar epithelial wound healing (A; t = 24 hours). Bars represent mean wound closure + SEM (number of pixels ×1000) of triplicate experiments (*p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001 vs. control). B. Differences in wound closure rate over time between incubation in control medium (0.1% FBS) and positive control medium (10% FBS). Points represent mean wound closure rate + SEM of triplicate experiments (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 vs control). C. Effect of addition of various concentrations of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from a term newborn diluted in control medium (0.1% FBS) on in vitro alveolar epithelial wound healing (t = 24 hours). Bars represent mean wound closure + SEM (% of control) of triplicate experiments (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 vs. control). D. Effects of various concentrations of albumin and BALF (diluted 1:10) from a term newborn (total protein in the original BALF specimen was 1.7 mg/ml). Bars represent mean wound closure + SEM relative to control medium of triplicate experiments (***p < 0.001 vs. control).
