Figure 4.
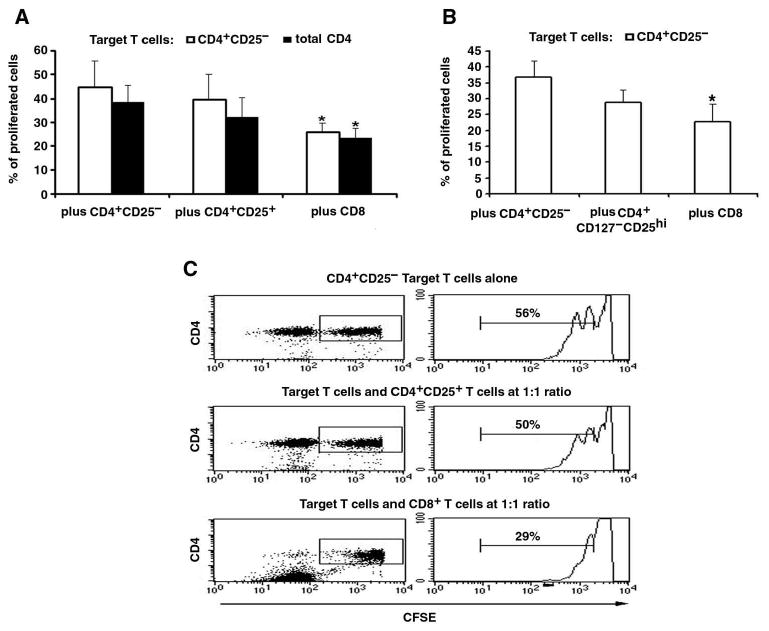
Post-transplant CD8 Treg cells have stronger suppressive function than their autologous CD4+CD25+ Treg cells.
A, As we did in Figure 3, post-transplant CD8 line T cells or CD4+CD25+ T cells sorted from autologous post-transplant CD4 line T cells were cocultured in contact, at the ratio of 1:1, with IL-2 stimulated autologous CD4 line T cells as a whole or CD4+CD25− T cells purified from it, as target. Results from three experiments are shown, and the bar represent the mean ± SD, * p < 0.05. B, As in panel A, post-transplant CD8 line T cells as a whole, or CD4+CD127−CD25high T cells that were sorted from autologous post-transplant CD4 line T cells, were cocultured in contact with IL-2 stimulated target cells (sorted autologous CD4+CD25− T cells), at the ratio of 1:1. * p <0.05. C, Representative histograms showing CFSE-labeled post-transplant, target CD4+CD25− T cells' proliferation when cocultured with autologous CD4+CD25+ T cells or CD8 T cells. Proliferation (CFSE dilution) of gated CD4 T cells was assessed by flow cytometry after co-culturing for 4 days (see Methods).
