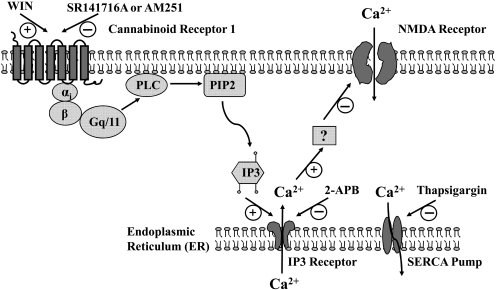
Fig. 9.
Schematic illustration of the calcium signaling pathways that are modulated by the cannabinoid system. Activation CB1 receptors mobilizes the IP3 pathway through a G protein-coupled process. Activation of IP3 receptors triggers calcium release from intracellular calcium stores, which in turn inhibits calcium influx mediated by activated NMDA receptor channels or by voltage-dependent calcium channels (data not shown). Depletion of intracellular calcium stores by SERCA pump inhibitor or blocking calcium release from intracellular calcium stores by IP3 receptor inhibitors prevents the cannabinoid from inhibiting the calcium influx related to the excitotoxicity of neurons and development of neuropathic pain. How the calcium release from intracellularly stores leads to the inhibition of NMDA receptors and/or voltage-dependent calcium channels remains to be determined.