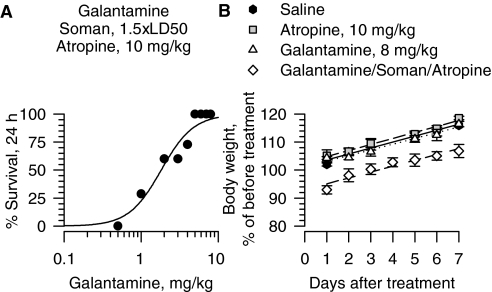
Fig. 1.
Pretreatment with galantamine prevents the acute toxicity of 1.5 × LD50 soman in guinea pigs post-treated with atropine. A, dose-response relationship for galantamine to afford 24-h survival of guinea pigs challenged with 1.5 × LD50 soman (42 μg/kg s.c.) and post-treated with atropine (10 mg/kg i.m.). Galantamine (0.5–8 mg/kg i.m.) was injected in one of the hind limbs of the animals 30 min before soman. Atropine was injected in the other hind limb 1 min after the nerve agent. Each group consisted of 8 to 12 animals. “% survival” represents the percentage of animals that were kept alive at 24 h after the soman challenge because they presented no life-threatening symptoms. B, body weight of animals subjected to different treatments. Body weights are expressed as percentage of the weights measured 1 h before the first treatment. Experimental groups consist of animals that were treated with 1) saline (0.5 ml/kg i.m.), 2) atropine (10 mg/kg i.m.), 3) galantamine (8 mg/kg i.m.), or 4) galantamine (8 mg/kg i.m.) followed 30 min later by 1.5 × LD50 soman (42 μg/kg s.c.), and atropine (10 mg/kg i.m.) 1 min after soman. Each experimental group consisted of five to eight animals. Data points and error bars represent mean and S.E.M., respectively. Solid, dotted, and dashed lines are the linear regression of each data set. Adapted from Albuquerque EX, Pereira EFR, Aracava Y, Fawcett WP, Oliveira M, Randall WR, Hamilton TA, Kan RK, Romano JA Jr, and Adler M (2006) Effective countermeasure against poisoning by organophosphorus insecticides and nerve agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13220–13225. Copyright © 2006. National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A.