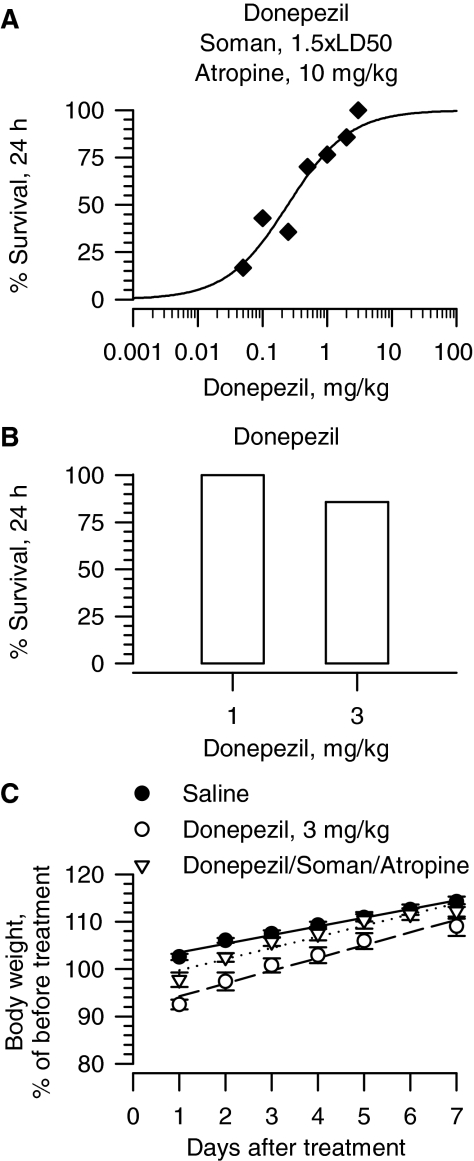
Fig. 2.
Effectiveness of donepezil in preventing toxicity of 1.5 × LD50 soman in atropine-treated guinea pigs. A, dose-response relationship for donepezil to afford 24-h survival of guinea pigs challenged with 1.5 × LD50 soman (42 μg/kg s.c.) and post-treated with atropine (10 mg/kg i.m.). Donepezil (0.05–3 mg/kg i.m.) was injected in one of the hind limbs of the animals at 30 min before soman. Atropine (10 mg/kg i.m.) was injected in the other hind limb 1 min after the nerve agent. Each group consisted of 8 to 12 animals. “% survival” represents the percentage of animals that were kept alive at 24 h after the soman challenge because they presented no life-threatening symptoms. B, survival of guinea pigs treated with donepezil alone (1 or 3 mg/kg). C, body weight of animals subjected to different treatments. Body weights are expressed as percentage of the weights measured 1 h before the first treatment. Experimental groups consist of animals that were treated with 1) saline (0.5 ml/kg i.m.), 2) donepezil (3 mg/kg i.m.), or 3) donepezil (3 mg/kg i.m.) followed 30 min later by 1.5 × LD50 soman (42 μg/kg s.c.) and atropine (10 mg/kg i.m.). Data points and error bars represent mean and S.E.M., respectively, of results obtained from 18 animals in the saline group and 5 to 8 animals in the other two experimental groups. Solid, dotted, and dashed lines are the linear regression of each data set; r2 ranged from 0.96 to 0.98.