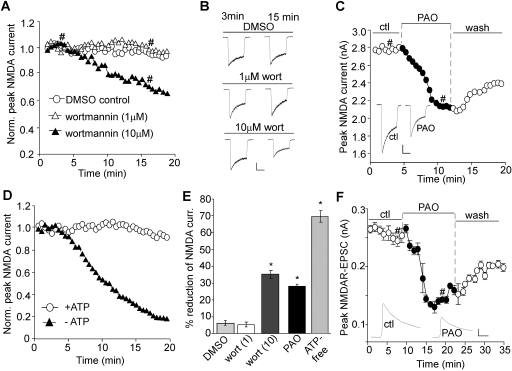
Fig. 1.
Blocking PIP2 synthesis reduces NMDAR-mediated currents. A, C, and D, plot of peak NMDA (100 μM)-evoked currents showing the effect of wortmannin dialysis (1 and 10 μM; A), PAO perfusion (10 μM; C), or an ATP-free internal (D) in dissociated cortical pyramidal neurons. B and C (inset), representative current traces (at 3 and 15 min denoted by #). Scale bars, 0.5 nA, 1 s. E, cumulative data (mean ± S.E.) showing the percentage reduction of NMDAR currents by various agents.∗, p < 0.001, ANOVA, compared with DMSO control. F, plot of NMDAR-EPSC in cortical slices showing the effect of PAO (10 μM) perfusion. Each point represents the average peak (mean ± S.E.) of three consecutive NMDAR-EPSCs. Inset, representative NMDAR-EPSC traces (at time points denoted by #). Scale bars, 0.05 nA, 50 ms.