Fig. 1.
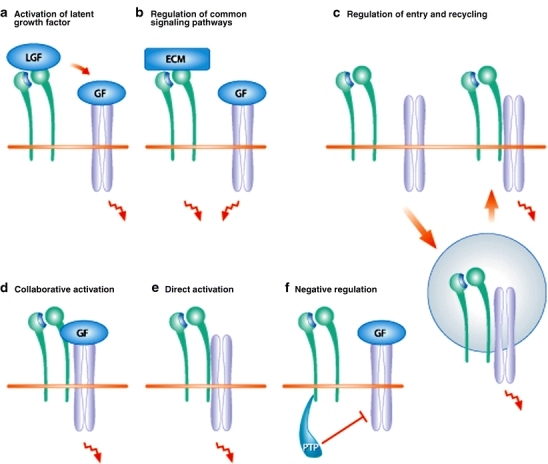
Various forms of collaboration between integrins (green) and growth factor receptors (blue). a Integrins may directly bind to latent growth factors (LGF) and activate them. Subsequently, activation growth factors (GF) can bind to their signaling receptors. b The binding of integrins to extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins often activates the same signaling pathways as GF binding to GF receptors. c Receptors can signal when located either on the cell surface or in endosomes. Co-endocytosis of integrins and GF receptors regulates cellular signaling at multiple levels. d, e Integrins can activate GF receptors in a collaborative or direct manner. In both cases, integrins create an environment in which the GF receptors can properly interact with the downstream signaling molecules. In the collaborative mechanism, the binding of GFs to their receptors precedes receptor activation (d), whereas in the direct mechanism, the GF receptors are activated without ligand binding (e). f Integrins can also activate protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTP) and suppress signaling by GF receptors
