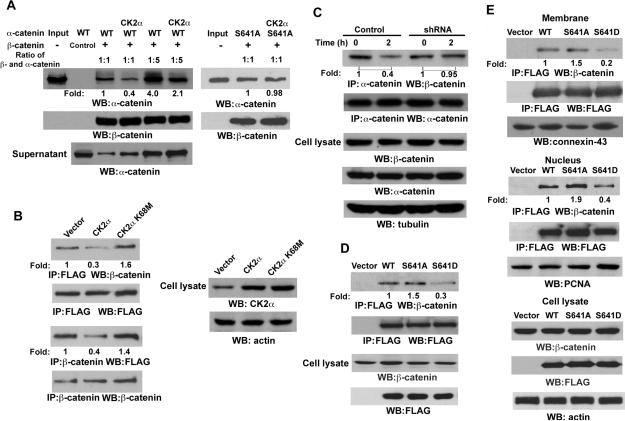
Figure 3. CK2 α-mediated Phosphorylation of α-catenin at S641 Releases α-catenin from Binding to α-catenin.
Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies.
(A) In vitro kinase assays were performed with purified bacterially expressed WT His-α-catenin with or without CK2α, which is followed by GST pull-down analyses with GST (control) or GST-α-catenin glutathione-agarose beads.
(B) FLAG-tagged α-catenin was co-transfected with pRc/CMV2-HA-CK2α or pRc/CMV2-HA-CK2α K68M into 293T cells.
(C) A431 cells expressing with or without CK2α shRNA were treated with or without EGF (100 ng/ml) for 2 hr.
(D) FLAG-tagged WT α-catenin, α-catenin S641A, or α-catenin S641D mutant were transfected into 293T cells. Immunoprecipitation of the total cell lysate with an anti-FLAG antibody was followed by immunoblotting analyses with the indicated antibodies.
(E) FLAG-tagged WT α-catenin, α-catenin S641A, or α-catenin S641D mutant were transfected into 293T cells. Immunoprecipitation of the membrane or nucleus fraction was performed with the indicated antibodies.