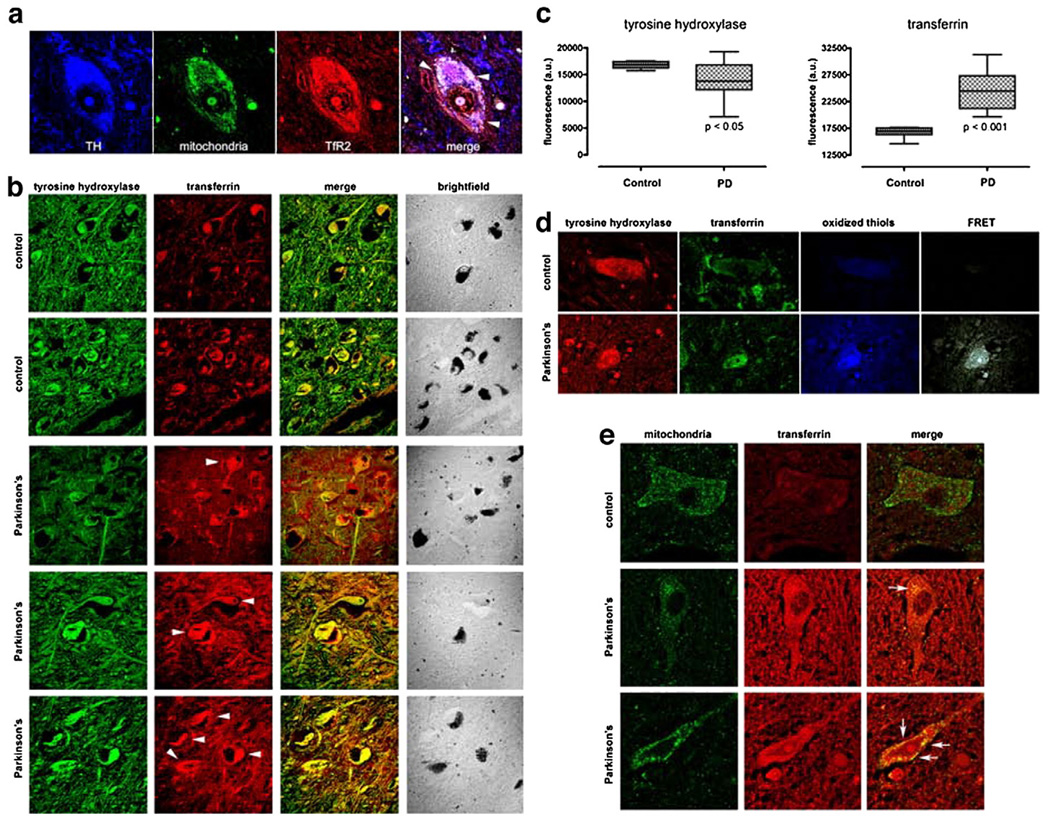
Fig. 7.
(a) As in the rat brain, TfR2 is localized to dopamine neurons in the human brain and it colocalizes, in part, with mitochondria (arrow-heads). (b) There is a marked increase in Tf in substantia nigra dopamine neurons – which contain neuromelanin (brightfield) – and in the surrounding neuropil in Parkinson's disease compared to controls. (c) Quantification of TH and Tf fluorescence intensity in PD cases (n=6) and controls (n=4) reveals that a statistically significant decrease in TH immunoreactivity is paralleled by a significant increase in Tf levels. (d) In Parkinson's disease, there is thiol oxidation of Tf, as indicated by FRET between oxidized thiols (anilino-naphtalene sulfonate maleimide) and Tf (see Fig. 3). (e) In the dopamine neurons, some of the Tf is colocalized with mitochondria. Human substantia nigra sections were triple labeled for tyrosine hydroxylase (not shown), mitochondria and Tf (arrow-heads).