Fig. 5.
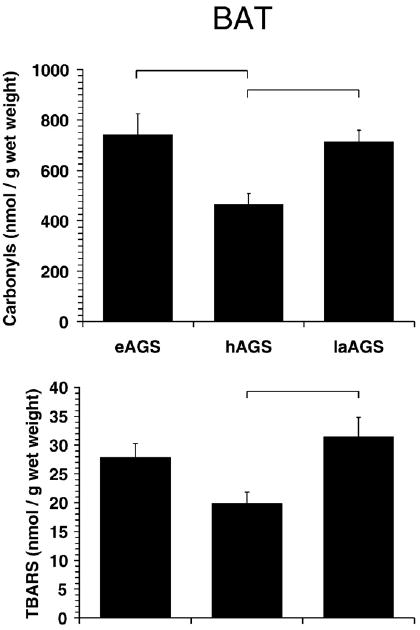
Oxidative stress is highest in BAT after arousal and during euthermy. Levels of carbonyl proteins were less in hAGS compared to laAGS (p<0.02, SNK, n=5) and compared to eAGS (p<0.02, SNK, n=5). Levels of TBARS were also less in hAGS compared to laAGS (p<0.05, Dunn's method, n=4–5) as indicated by horizontal bars. Data from animals treated with AO prior to arousal are described below, but not shown because AO did not affect any of the parameters measured. Level of protein carbonyls in BAT from animals treated with AO prior to arousal was 608±52 nmol/g wet mass and was not significantly different from late arousal (laAGS) animals treated with saline prior to arousal (p>0.30, t-test, n=5). Similarly, level of TBARS in animals treated with AO prior to arousal was 37±7.1 nmol/g wet mass and was not significantly different from laAGS treated with saline prior to arousal (p>0.5, t-test, n=5).
