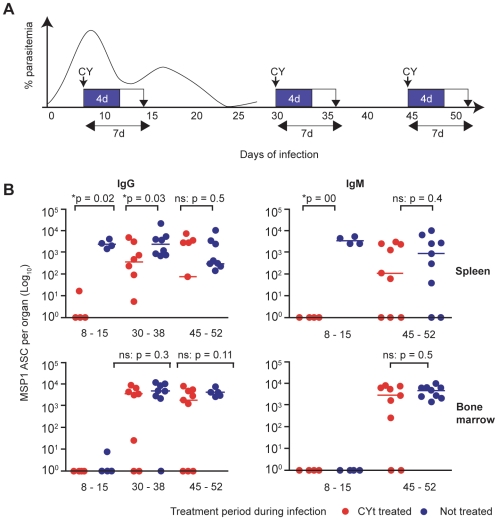
Figure 4. Intrinsically long-lived MSP119-specific IgG and IgM ASC are generated in a primary infection.
(A) Cartoon showing the time course of the experiment. C57BL/6 mice were infected with 105 P. chabaudi iRBC, and received either 140 mg Cyclophosphamide (CY) per Kg body weight (over 4 days), or normal saline (control) at days 8, 30 and 45. Sampling of spleens and bone marrows were carried out 7 days later at days 15, 38 and 52 days. The numbers of splenic and bone-marrow IgG ASC were determined by ex vivo ELISpot assays as described in the experimental procedures. (B) Left panel, Comparison of numbers of MSP119-specific IgG ASC between control treated mice (blue circles) and CY treated mice (red circles) at days 8–15 (n = 4), 30–38 (n = 8) and 45–52 (n = 9). Right panel, Comparison of numbers of MSP119-specific IgM ASC between CY treated and control mice at 8–15 (n = 4) and 45–52 (n = 9) time intervals of treatment and sampling. (No MSP119-specific ASC were detected in the bone marrow at day 15). Background values from naive uninfected mice have been subtracted from all the values shown as described in Figure 1. Each symbol represents an individual mouse, and the horizontal bars indicate the median values of 8 mice. The numbers of ASC in the two groups at each time point were compared using a Mann Whitney test; * indicates the differences were significant (p values are shown), and ns no significant differences.