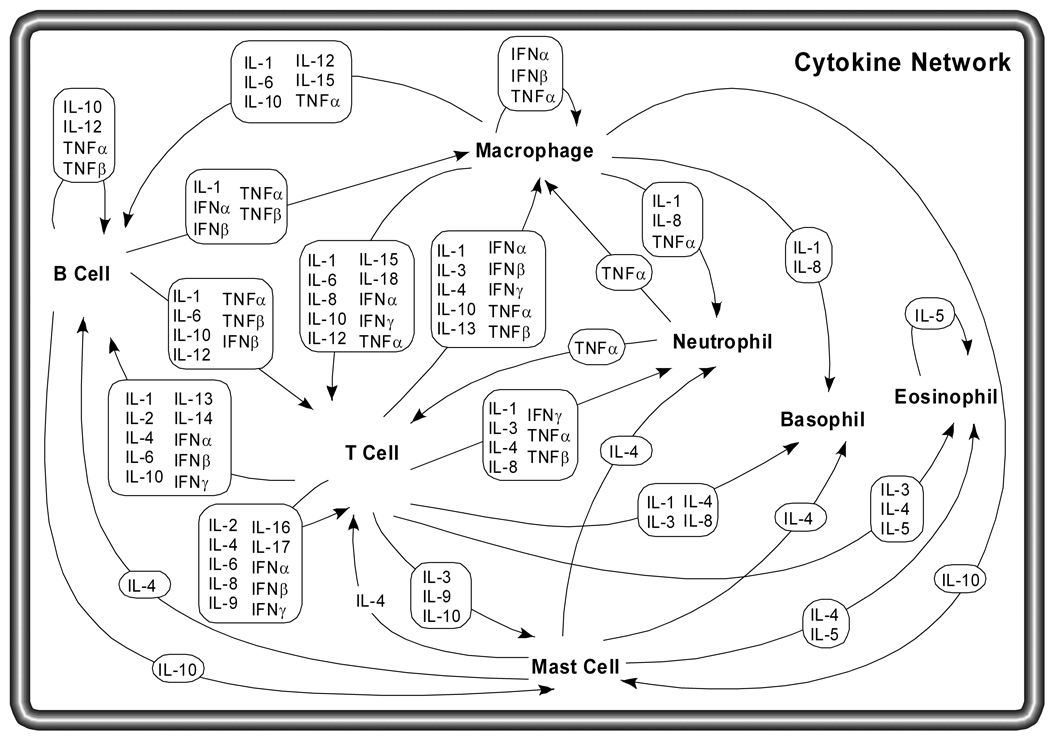
Figure 1.
Cytokine network. Several different cell types coordinate their efforts as part of the immune system, including B cells, T cells, macrophages, mast cells, neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils. Each of these cell types has a distinct role in the immune system, and communicates with other immune cells using secreted cytokines. Macrophages phagocytose foreign bodies and are antigen-presenting cells, using cytokines to stimulate specific antigen dependent responses by B and T cells and non-specific responses by other cell types. T cells secrete a variety of factors to coordinate and stimulate immune responses to specific antigen, such as the role of helper T cells in B cell activation in response to antigen. The proliferation and activation of eosinophils, neutrophils and basophils respond to cytokines as well.