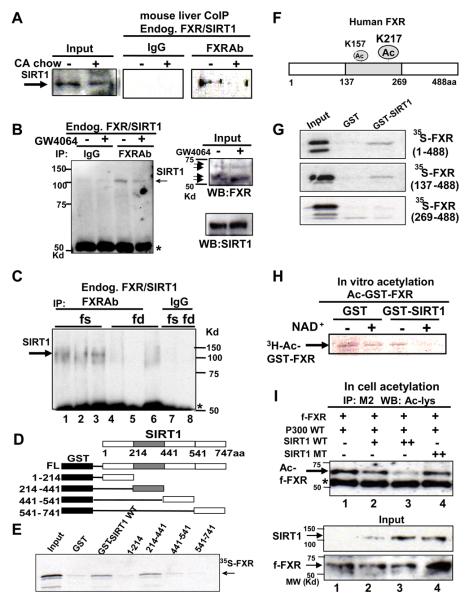
Fig. 4. SIRT1 directly interacts with and deacetylates FXR.
A-C) Mice were fed normal or CA chow (+) for 6 hr (A) or treated with vehicle (−) or GW4064 (+) for 1 hr (B) or fasted (fs) overnight or refed (fd) after overnight fasting (C). CoIP studies were performed to examine FXR/SIRT1 interaction. D) Schematic diagrams of GST-SIRT1 full length (FL) and deletion mutants. The gray shaded area represents the sirtuin homology domain. E) 35S-FXR was synthesized in vitro, and GST pull down assays were performed. F) A schematic diagram of FXR acetylation sites. G) 35S-FXR full length wild type and mutants were synthesized, and binding to GST-FXR fusion proteins was determined. H) GST-FXR, which had been acetylated using p300 with 3H-acetyl CoA, was incubated with eluted GST or GST-SIRT1 and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by fluorography. I) Cos-1 cells were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids and treated with deacetylase inhibitors for 3 hr. Flag-FXR levels were immunoprecipitated and acetylated flag-FXR was detected by western analysis. Acetylated flag-FXR and IgG heavy chain are indicated by arrow and asterisk, respectively. SIRT1 and flag-FXR levels in input are shown.