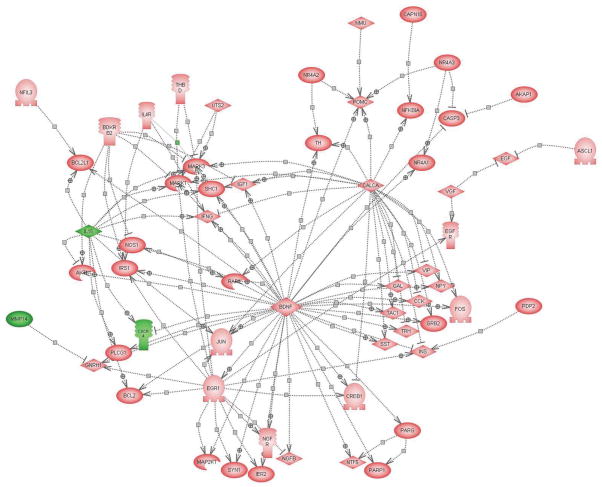
Figure 5.
Putative targets of common changes in gene expression with single and repeated IMO stress. Pathway analysis showing the common targets which are activated or inhibited by the common genes which are decreased (green, IL15, MMP14, CXCR4) or elevated (pink, all others) or by both durations of IMO stress. The symbols are as described in figure above. The abbreviations are as follows: PARP1 [ADP-ribosyltransferase (NAD+; poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase)]; BCL2 (B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2); BCL2L1 (Bcl2-like 1); BDKRB2 (bradykinin receptor B2); BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor); CALCA (calcitonin/calcitonin-related polypeptide, alpha); CREB1 (cAMP responsive element binding protein 1); CASP3 (caspase 3); CD44 (CD44 antigen); CCK (cholecystokinin); EGR1 (early growth response 1); EGF (epidermal growth factor); EGFR (epidermal growth factor) FOS (FOS oncogene); GAL (galanin); GNRH1 (gonadotropin-releasing hormone 1); GRB2 (growth factor receptor bound protein 2); IER2 (immediate early response 2); INS (insulin); IRS1 (insulin receptor substrate 1); IGF1 (insulin-like growth factor 1); IFNG (interferon, gamma); IL15 (interleukin 15); IL4R (interleukin 4 receptor); JUN (Jun oncogene); MMP14 (matrix metalloproteinase 14); MMP9 (matrix metalloproteinase 9); MAPK1 (mitogen activated protein kinase 1); MAPK3 (mitogen activated protein kinase 3); MAP2K1 (mitogen activated protein kinase kinase 1); RAF1 (murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1); NGFR (nerve growth factor receptor); NMU (neuromedin U); NPY (neuropeptide Y); NTF5 (neurotrophin 5); NOS1 (nitric oxide synthase 1); NFIL3 (nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated); NR4A1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1); NR4A2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2); NR4A3 (nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3); PARG [poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase]; POMC (proopiomelanocortin); PDP2 (pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase isoenzyme 2); SST (somatostatin); SHC1 (src homology 2 domain-containing transforming protein C1); SYN1 (synapsin I); TAC1 (tachykinin, precursor 1); THBD (thrombomodulin); AKT1 (thymoma viral proto-oncogene 1); TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone); TGFB1 (transforming growth factor, beta 1); TNF (tumor necrosis factor); TH (tyrosine hydroxylase); UTS2 (urotensin 2); VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor); VIP (vasoactive intestinal peptide); VGF (VGF nerve growth factor inducible).