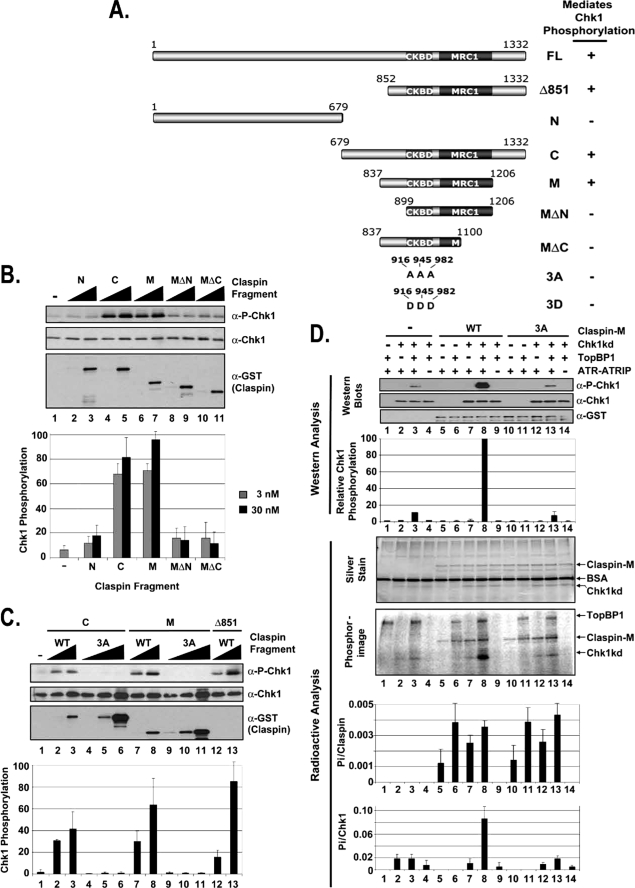
FIGURE 5.
Identification of the minimal functional domain in Claspin. A, schematic of the Claspin fragments and summary of their ability to mediate Chk1 phosphorylation by ATR. The locations of the putative phosphorylation site mutations at Thr916, Ser945, and Ser982 (3A and 3D) in the CKBD are indicated. The Mrc1-like domain (MRC1, amino acids 1045–1203) is defined in the Pfam protein families data base as a putative domain of average length of 142.3 amino acids that is found to be the most conserved region in Mrc1 (31). B, stimulation of ATR phosphorylation of Chk1 by Claspin fragments. Kinase assays were carried out with ATR-ATRIP, HisChk1-kd, and TopBP1 as described in the legend for Fig. 1 except with 0, 3, or 30 nm of the indicated Claspin fragment. The error bars indicate the average deviation from the mean. α-P-Chk1, phospho-Chk1. C, mutations in the Chk1-binding domain of the Claspin fragments abolish their ability to stimulate ATR phosphorylation of Chk1. Kinase assays were carried out with ATR-ATRIP, HisChk1-kd, and TopBP1 as described in B except with 0, 3, 30, or 300 nm of the indicated Claspin fragment. D, kinase assays were carried out with ATR-ATRIP, Chk1-kd, and TopBP1 as described in the legend for Fig. 1 except with the addition of [γ-32P]ATP to monitor the total phosphorylation in the reaction. 25 nm wild-type (WT) Claspin-M fragment or the Claspin-M fragment containing alanine mutations in the putative phosphorylation sites (3A) were included into the reactions as indicated. Half of the kinase reaction was loaded onto a gel for analysis by immunoblotting for phospho-Chk1 and Chk1, and the other half of the reaction was loaded onto a separate gel for analysis by silver staining and phosphorimaging as indicated. BSA, bovine serum albumin.