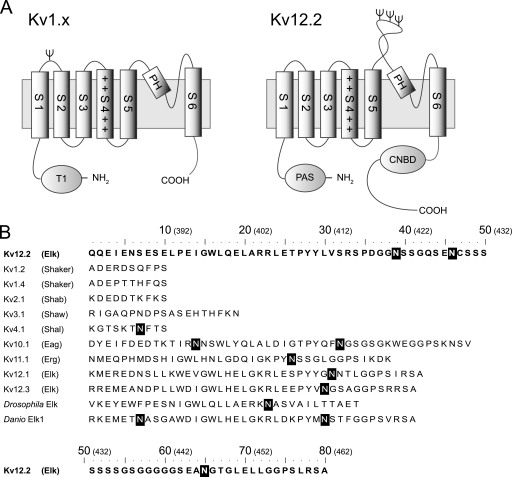
FIGURE 1.
Topological model and amino acid sequence of S5-P loops of various voltage-dependent potassium channels. A, the proposed topology of the Kv1.x and Kv12.2 monomers is shown. Kv channels have six transmembrane segments (S1-S6). Helix S4 contains positively charged residues, indicated by +. The predicted N-linked glycosylation sites are indicated by Ψ. Kv1.x channels have an N-terminal tetramerization domain (T1), and single N-glycosylation site between helix S1 and S2 with the exception of Kv1.6. Kv12.2 channels have an N-terminal Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) domain and a C-terminal cyclic nucleotide biding domain (CNBD). Kv12.2 has three N-glycosylation sites in a particularly long extracellular S5-P loop between helix S5 and the pore helix (PH). B, shown are amino acid sequences of the predicted S5-P loops of the mouse Kv, fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) Elk, and zebrafish (Danio rerio) Elk1 channels. The names in parentheses refer to the subfamilies containing the corresponding mouse Kv channels. Elk, Eag, and Erg are subfamilies of the EAG family. White letters in black boxes indicate the predicted N-linked glycosylation consensus sequence Asn-Xaa-(Ser/Thr) in which Xaa can be any amino acid except proline. The numbers in parentheses above the sequences indicate the positions of the residues in Kv12.2.