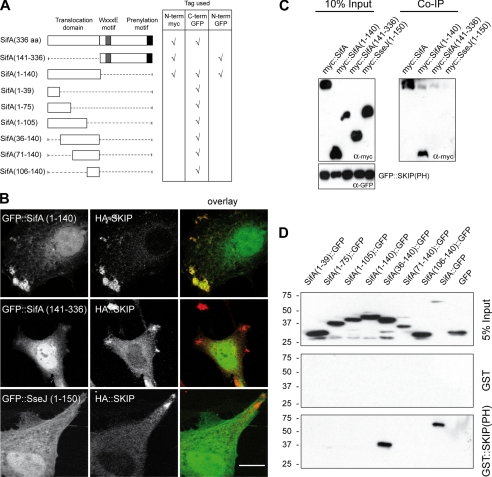
FIGURE 1.
The N-terminal domain of SifA interacts with the PH domain of SKIP. A, schematic representation of SifA and the truncated constructs used in this study and the location of the Myc or GFP fusion tags. B, intracellular localization of SifA-derived polypeptides and SKIP. HeLa cells expressing HA::SKIP and GFP::SifA-(1–140), GFP::SifA-(141–336), or GFP::SseJ(1–150) were immunostained for HA. Confocal images show GFP fusion polypeptides (green) and HA::SKIP (red) (scale bar: 10 μm). C, SKIP(PH) immunoprecipitates the N-terminal domain of SifA. Cell lysates prepared from HeLa cells expressing GFP::SKIP(PH) and Myc::SifA, Myc::SifA-(1–140), Myc::SifA-(141–336), or Myc::SseJ-(1–150) were incubated with rabbit anti-GFP antibody and Protein A beads. Co-immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-Myc antibody. D, GST::SKIP(PH) pulls down SifA-(36–140)::GFP. GST::SKIP(PH) or GST were immobilized on beads and incubated with extracts of HeLa cells expressing GFP, SifA::GFP, and various SifA truncated variants fused to the N terminus of GFP. Bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-GFP antibody.