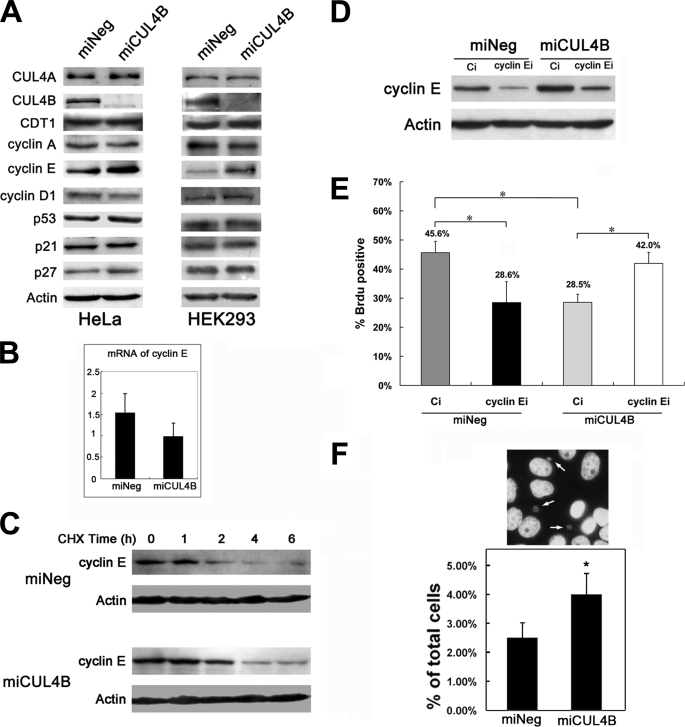
FIGURE 6.
CUL4B knockdown results in accumulation of cyclin E. A, protein levels of representative CUL4 targets, including cyclin E. CUL4B knockdown causes an elevation in cyclin E. Cells were harvested, and equal amounts (60 μg) of total cell lysates of the indicated asynchronous cells were subjected to SDS-PAGE (12%) and detected with the indicated antibodies. B, in parallel, the mRNA levels of cyclin E in each group of asynchronous HeLa cells were measured by real-time PCR. C, increased half-life of cyclin E in CUL4B RNAi cells. Cells were treated with cycloheximide (50 μg/ml) and harvested at the indicated time points. Equal amounts (60 μg) of total cell lysates of the indicated cells were analyzed by Western blotting assays. D, RNAi of cyclin E reduced the overaccumulation of cyclin E caused by the RNAi of CUL4B. The indicated cells were transfected with cyclin E siRNA (cyclin Ei) or control siRNA (Ci). 48 h after transfection, cyclin E protein expression was analyzed by Western blotting. E, alleviation of the cell proliferation defects in CUL4B and cyclin E co-silenced cells. The indicated cells were transfected with cyclin E siRNA or control siRNA. 24 h after transfection, cells were synchronized at the G1/S boundary by a double-thymidine block and then were released into the cell cycle. 1.5 h later, cells were analyzed by a BrdUrd incorporation assay. Results represent means ± S.D. from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.001. F, RNAi of CUL4B increases micronuclei formation in HeLa cells. The results are shown as the percentage of cells showing micronuclei formation. Bars, means ± S.D. *, p < 0.01 versus miNeg.