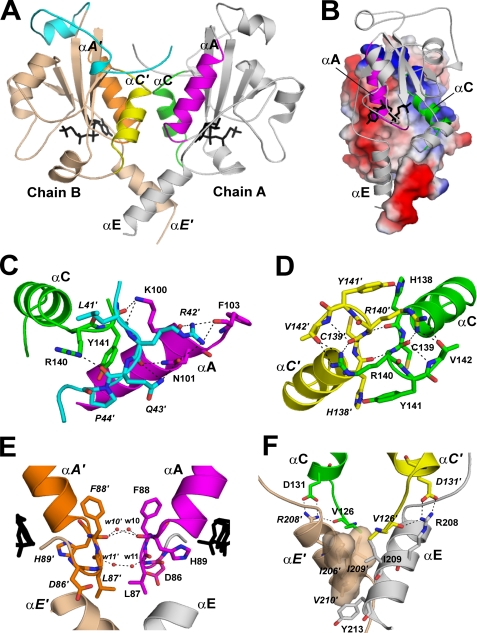
FIGURE 4.
Inter-subunit contacts at the CCT236 dimer interface. A, CCT dimer interface. In chain A, the structural elements of the dimer interface are labeled αA (residues 86–103; magenta), αC (residues 126–142; green), and αE (residues 203–215; gray). In chain B, the elements are labeled αA′ (residues 86–103; orange), αC′ (residues 126–142; yellow), and αE′(residues 203–216; wheat). Segment N (residues 40–75) of chain B is highlighted in cyan. These dimer interface elements are color-coded for reference to the detailed views shown in C–F, where the residues involved in the inter-chain interaction are shown in stick representation, and interactions (<3.5 Å) are indicated by dashed lines. B, surface electrostatic potential of chain B showing charge complementarity at the dimer interface. Chain A is shown in ribbon format. C, interactions between segment N (cyan) of chain B (residues 41–44) with αA (magenta) and the L3 loop following αC (green) in chain A. D, direct interactions between the L3 loops that harbor the conserved 140RYVD motif. Chain A is in green and chain B in yellow. E, interactions between the L1 loops involving ordered waters and main chain atoms at Leu-87 and Phe-88. Chain A is in magenta and chain B in orange. A portion of each CDP-choline proximal to the L1 loop is shown in black stick representation. The water molecules are labeled by the last two digits of their ID numbers in the PDB entry. F, interaction between αE and αE′ is mediated by hydrophobic residues that form complementary binding surfaces. The Arg-208 side chain in αE is anchored to αC′ by interactions with Val-126 and Asp-131.