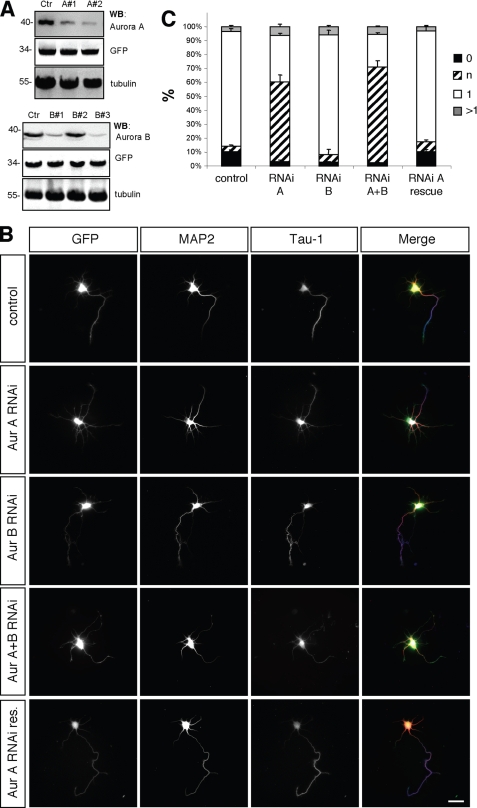
FIGURE 3.
Aurora A is required for neuronal differentiation. A, HEK 293T cells were transfected with vectors for EGFP, rat Aurora A (upper panel) or rat Aurora B (lower panel), and pSHAG-1 or vectors for shRNAs directed against Aurora A (A1, A2) or Aurora B (B1, B2, or B3) as indicated. Aurora A and B expression was analyzed by Western blotting (WB) using antibodies specific for Aurora A or Aurora B, GFP (transfection control), and α-tubulin (loading control). Numbers indicate molecular mass in kDa. B, hippocampal neurons were transfected at 0 d.i.v. with vectors for GFP, pSM2 (control), shRNAs directed against Aurora A (Aur A RNAi: sh-Aurora A2), Aurora B (Aur B RNAi: sh-Aurora B3), Aurora A and B (Aur A+B RNAi: sh-Aurora A2 + B3), or human GFP-Aurora A (Aur A RNAi res.) as indicated. Transfected cells were analyzed at 3 d.i.v. by staining with an anti-MAP2 (red) and the Tau-1 (blue) antibody. Scale bar, 40 μm. C, the development of neuronal polarity was analyzed by determining the number of unpolarized neurons without an axon (0, black bars), unpolarized neurons with one or more neurites of undefined identity (indeterminate neurites longer than 50 and weak of absent Tau-1 staining; n, hatched bars), polarized neurons with a single axon (1, white bars), or neurons with multiple axons (>1, gray bars) (t test: multiple indeterminate neurites: p < 0.01, Aur A RNAi, Aur A+B RNAi compared with GFP; means ± S.E.). ANOVA (p < 0.0001) and a parametric Student's t test were used to test statistical significance.