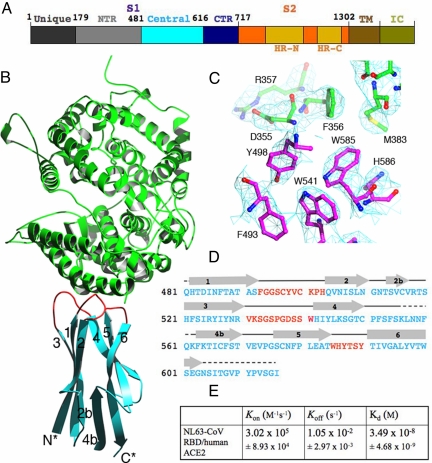
Fig. 1.
Structure of NL63-CoV RBD complexed with human ACE2. (A) Domain structure of the NL63-CoV spike protein. Unique, unique region; NTR, N-terminal region; Central, central region; CTR, C-terminal region; HR-N, heptad-repeat N; HR-C, heptad-repeat C; TM, transmembrane anchor; IC, intracellular tail. The unique domain only exists in NL63-CoV and is not involved in receptor binding (19, 20). (B) Overall structure of NL63-CoV RBD complexed with human ACE2. The RBD core is in cyan, RBMs in red, and ACE2 in green. (C) Averaged electron density map contoured at 1.0 σ and covering a portion of the NL63-CoV–ACE2 interface. (D) Sequence and secondary structures of NL63-CoV RBD. Beta-strands are drawn as arrows. RBMs are in red; the remainder of the RBD is in cyan. Disordered regions are shown as dashed lines. (E) Kinetics and binding affinity of NL63-CoV RBD and human ACE2 by surface plasmon resonance using Biacore. Structural illustrations were made using Povscript (31).