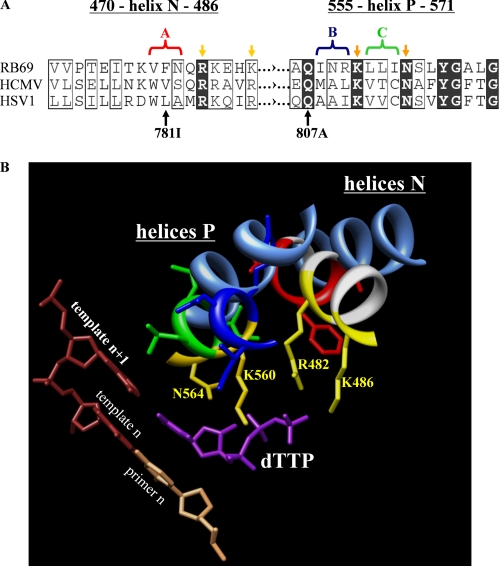
FIGURE 2.
Structure-based correlation between the nucleotide-binding sites of related RB69, HSV-1, and HCMV polymerases. A, sequence alignment of critical regions of helix N and helix P of DNA polymerases from HSV-1, HCMV, and RB69. Conserved residues are highlighted in black, and similar residues are boxed (61). Yellow arrows point to the amino acid residues of RB69 gp43 that interact with the triphosphate. Light and dark yellow color code distinguishes between residues of helix N and P, respectively. The amino acid substitutions V781I and Q807A illustrate previously reported mutations associated with resistance to foscarnet in HCMV (42, 62). The color-coded brackets and the corresponding captions “A, B, and C” illustrate the groups of three amino acids of the HCMV polymerase that were replaced in this study. The color code used in A is the same as in B. B, crystal structure of RB69 DNA polymerase in complex with a nucleotide substrate and primer-template (PDB code 1IG9). The amino acid residues of RB69 gp43 that interact with the triphosphate are highlighted in yellow. The cornflower blue ribbons represent the helices N and P of the HSV-1 polymerase. The crystal structure of HSV-1 polymerase in its apo form (PDB code 1GV9) was aligned with the crystal structure of RB69 polymerase (PDB code 1IG9).