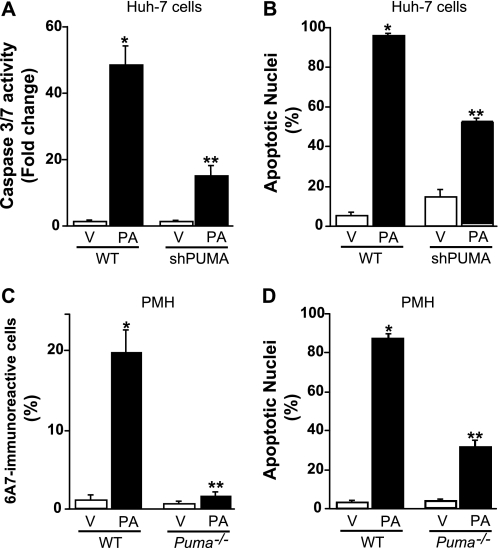
FIGURE 8.
PUMA contributes to palmitate-mediated apoptosis. A and B, Huh-7 (WT) and Huh-7 cells stably expressing short hairpin RNA complementary to PUMA (shPUMA) were incubated for 24 h with palmitic acid (PA) at 800 μm; Vehicle (V)-treated cells were used as control. A, caspases 3 and 7 catalytic activity was assessed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” B, apoptotic nuclei were counted according to morphological criteria after 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride staining. Data represent the mean and S.E. of three experiments; *, p < 0.05, palmitate-treated cells versus vehicle-treated cells; **, p < 0.01, palmitate-treated shPUMA versus palmitate-treated WT. C, primary murine hepatocytes (PMH) isolated from WT or Puma−/− mice were treated for 8 h with vehicle or palmitic acid (400 μm). Bax activation was assessed as described under “Experimental Procedures,” and 6A7-immunoreactive cells were quantified in 12 random 40× objective fields for each condition with automated software. Data represent the mean and S.E. of three experiments; *, p < 0.01, palmitate-treated cells versus vehicle-treated cells; **, p < 0.01, palmitate-treated Puma−/− versus palmitate-treated WT. D, primary murine hepatocytes isolated from WT or Puma−/− mice were treated for 24 h with vehicle or palmitic acid (200 μm). Apoptotic nuclei were counted according to morphological criteria after 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride staining. Data represent mean and S.E. of three experiments; *, p < 0.01, palmitate-treated cells versus vehicle-treated cells; **, p < 0.01, palmitate-treated Puma−/− versus palmitate-treated WT.