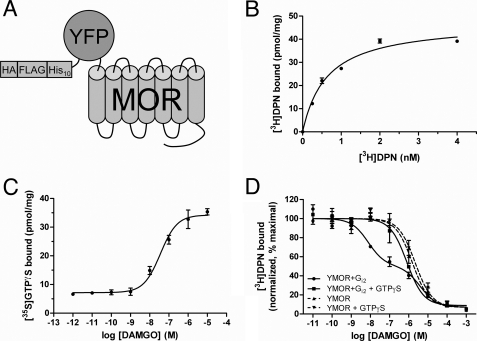
FIGURE 1.
Functional expression of a modified MOR in insect cells. A, schematic representation of the modified μ-opioid receptor expressed in insect cells. N-terminal modifications included a hemagglutinin signal sequence (HA), FLAG epitope, His10, and a YFP. This construct, termed YMOR, was expressed in Sf9 and HighFiveTM insect cells using a recombinant Baculovirus system. B, YMOR expressed in insect cells exhibits high affinity ligand binding. Plasma membrane preparations (5 μg) of HighFiveTM cells expressing YMOR were used in [3H]diprenorphine saturation binding assays. YMOR bound [3H]DPN with a Bmax of ∼40 pmol/mg and a Kd of 0.6 ± 0.1 nm. C, YMOR couples to G protein in insect cell membranes. Membrane preparations (2 μg) of HighFiveTM cells co-expressing YMOR and Gi2 heterotrimer were incubated with increasing concentrations of the μ-opioid agonist DAMGO in the presence of 10 nm [35S]GTPγS (isotopically diluted). DAMGO stimulated [35S]GTPγS exchange on Gαi2 with an EC50 of 36 ± 0.1 nm. D, agonist binding to YMOR expressed in insect cells is allosterically regulated by G proteins. YMOR/Gi2 membrane preparations (2–3 μg) were incubated with 0.8 nm [3H]DPN and increasing concentrations of DAMGO in the absence or presence of 10 μm GTPγS. A high affinity binding site for DAMGO (●, Ki hi = ∼2.9 nm) was disrupted in the absence of G protein coupling (with GTPγS, ■, Ki = ∼300 nM). DAMGO also displayed low affinity binding to membranes not expressing Gi2 (YMOR, ▴, Ki = ∼580 nm; and YMOR + GTPγS, ▾, Ki = ∼800 nm). Binding data were normalized to the curve fit maximum. For all panels the data are representative of at least two experiments performed in duplicate, and the error bars represent the standard error of the mean.