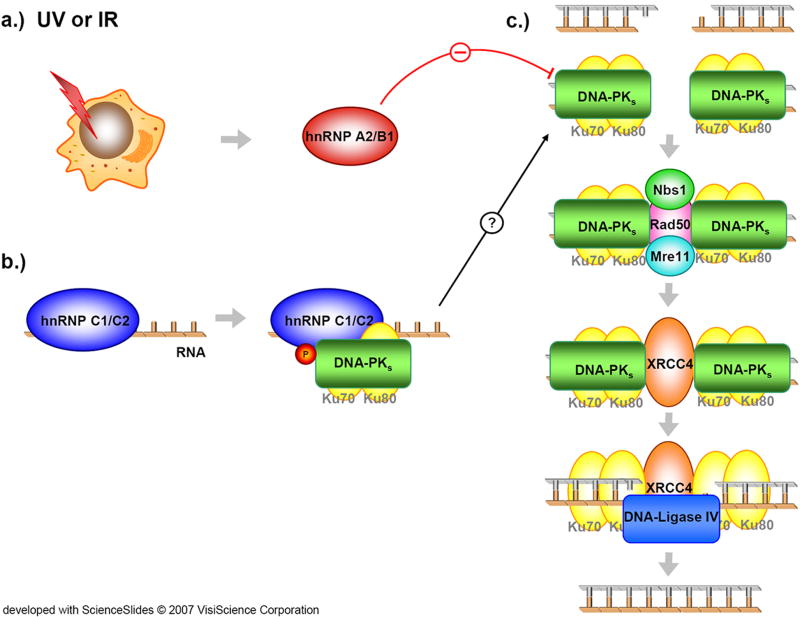
Figure 1. Non-homologous End Joining Repair (NHEJ).
NHEJ repairs DSB through an error prone mechanism available at any point during the cell cycle. As opposed to HR, NHEJ is less likely to lead to gross chromosomal rearrangements. a.) UV and IR are known to induce hnRNP A2/B1 protein which has been proposed to inhibit DNA-PK (Iwanaga et al., 2005). b.) hnRNP C is phosphorylated by a complex of DNA-PK and Ku proteins when it is bound to RNA transcript; the effect on NHEJ is unknown (Lee et al., 2005, Zhang et al., 2004). c.) The canonical NHEJ pathway is shown repairing a DSB beginning with DNA-PK and Ku protein binding, followed by Rad50 homologue (Rad50), Nirbrin (Nbs1), and meiotic recombination 11 homologue (Mre11) recruitment, displaced by X-ray repair in Chinese hamster cells 4 protein (XRCC4) which recruits DNA-Ligase IV culminating in the rejoining of the broken DNA strands (Weller et al., 2004)(Sonoda et al., 2006, Weinstock et al., 2006, Weller et al., 2004).