Figure 5. Abrogation of Conidial MLN Transport in CCR2 Depleter.
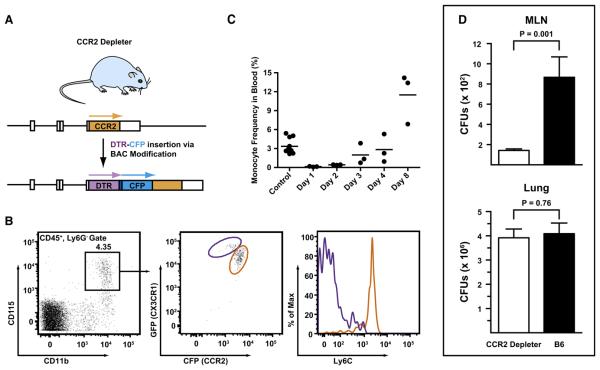
(A) Overview of BAC transgene. The BAC clone RP23-182D4 was modified to encode a simian DTR followed by a -(GSG)3GTG- linker, a 19 residue aphthovirus 2A cleavage site (-APVKQTLNFDLLKLAGDVESNPGP-) (Donnelly et al., 2001), and enhanced CFP under control of the CCR2 promoter. A stop codon was introduced at the 3′ transgene terminus followed by a single nucleotide deletion. Arrows indicate the expected translation products.
(B and C) Transgene expression by monocytes and sensitivity to DT. Transgene expression by monocytes and ablation by DT administration. (B) CD115+ blood monocytes (black gate, left) from CX3CR1 (gfp/+) CCR2 reporter mice were analyzed for CFP, GFP, and Ly6C expression. In the left panel, the purple and orange gates indicate GFPhiCFPlo and GFPloCFPhi monocytes, respectively. Ly6C expression by both subsets is shown in the histogram on the right. (C) CCR2 depleter mice were treated were 10 ng/g body weight DT via the i.p. route. The graph shows the percentage of CD115+ monocytes among CD45+ blood leukocytes at the indicate time points after DT treatment. Control mice include CCR2 depleter mice that did not receive DT and DT-treated nontransgenic littermates. One of two (B) or three (C) representative experiments is shown.
(D) CCR2 depleter mice (black bars) or control C57BL/6 mice (white bars) were treated with DT on day −1 and infected with 1–2 × 107 conidia on day 0. The histograms show the number (+ SEM) of MLN and lung CFUs 48 hr postinfection (n = 12–13/group).