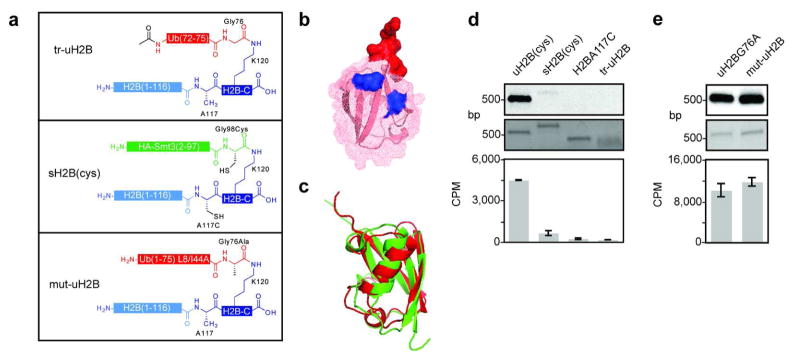
Figure 4. Structure activity relationship analysis of uH2B.
a, Schematic of semisynthetic uH2B structural variants. Top panel: H2B bearing the terminal five residues of ubiquitin attached to K120 (tr-uH2B); middle panel: H2B modified with HA-Smt3 with A117C/G98C mutations (sH2B(cys)); bottom panel: uH2BG76A with L8A/I44A double mutation (mut-uH2B). b, Ubiquitin structure (1UBQ) (48) represented by superimposed ribbon and mesh diagrams. The surface of the five residues of tr-uH2B are shown in red. Surfaces of L8 and I44 mutated to alanines in mut-uH2B are shown in blue. c, Structural alignment of ubiquitin (1UBQ) and Smt3 (1EUV) (37) shown in ribbon diagram. Structures and alignment rendered with PyMol. d, Dot1L methyltransferase assay on uH2B structural variants. Nucleosomes containing uH2B(cys), 6, sH2B(cys), H2B A117C, or tr-uH2B methylated with 3H SAM were separated on native gels and stained with ethidium bromide (middle panel) prior to probing for 3H methyl incorporation by fluorography (top panel). Quantification of methyltransferase activity was performed by filter-binding followed by liquid scintillation counting (bottom panel). e, Dot1L assay as in d, comparing uH2BG76A and mut-uH2B. Error bars represent one s.d. (n = 3–4).