Figure 3.
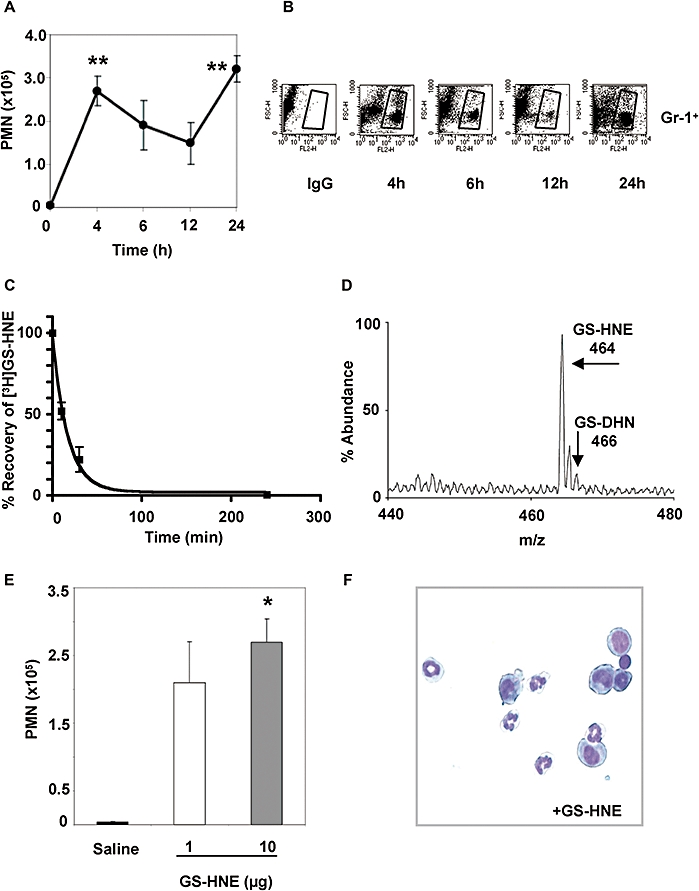
Characterization of GS-HNE-stimulated murine peritonitis. GS-HNE (10 µg) was injected intraperitoneally and peritoneal lavages were collected at indicated times. Total PMNs (A) were determined by differential analysis using Wright–Giemsa staining. In parallel, cells were stained with PE-conjugated anti-Gr-1 antibodies or IgG isotype control and used for FACS analysis (B). The recovery of [3H]GS-HNE from the peritoneal cavity was determined in the lavage at 0, 10, 30 and 240 min post injection (C). A representative mass spectrum of GS-HNE recovered from the peritoneum at 30 min post injection is shown in (D). For determining potency, GS-HNE was injected intraperitoneally at dose of 1 or 10 µg per mouse and exudates obtained after 4 h. Total leukocytes were determined by light microscopy and total PMNs (E) were determined as described above (representative histology shown in F). Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n= 3–5), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (vs. saline by one-way anova). GS-DHN, glutathionyl-1,4-dihydroxynonanol; GS-HNE, glutathionyl-4-hydroxy-trans-2-nonenal; PMN, polymorphonuclear leukocyte.
