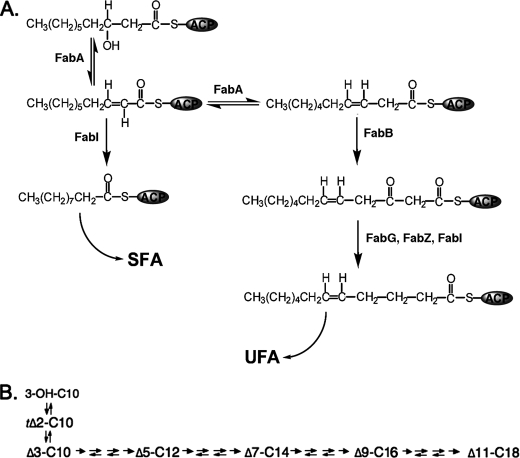
FIGURE 1.
UFA synthesis in E. coli. Panel A shows the reactions catalyzed by FabA and the proposed step catalyzed by FabB. Panel B shows the carbon flow in the UFA pathway. The arrows between each intermediate denote in order the 3-ketoacyl-ACP synthase (fabB or FabF), 3-ketoacyl-ACP reductase (FabG), the 3-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratase (FabZ), and the enoyl-ACP reductase (FabI). The first and last arrows denote irreversible reactions. The 3-ketoacyl-ACP synthase is truly irreversible due to decarboxylation, whereas FabI is reversible but the equilibrium lies very strongly in favor of reduction of the trans-2 double bond (21). The FabG and FabZ reactions are freely reversible (16).