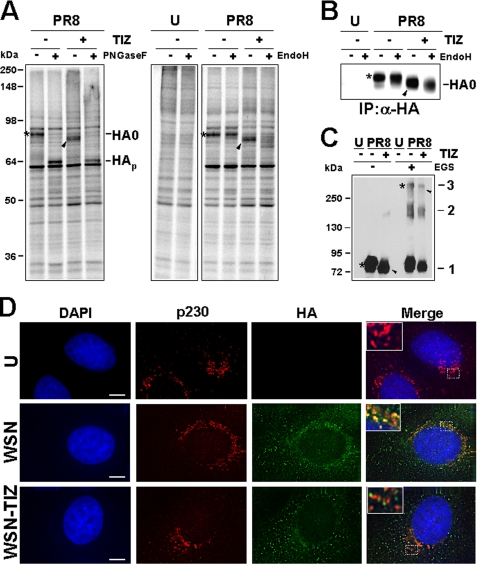
FIGURE 4.
Tizoxanide blocks HA maturation at an Endo-H-sensitive stage. A, mock infected (U) or PR8-infected MDCK cells treated with 10 μg/ml TIZ (+) or vehicle (−) after virus adsorption were labeled with [35S]Met/Cys (4-h pulse) at 5 h p.i. Radiolabeled proteins were digested (+) or not (−) with PNGase-F or Endo-H and processed for SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Uncleaved glycosylated (HA0) and nonglycosylated (HAp) hemagglutinin precursor forms are indicated. B, MDCK cells treated as in A were labeled with [35S]Met/Cys (4-h pulse) at 6 h p.i. Radiolabeled proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HA antibodies (α-HA), digested (+) or not (−) with Endo-H, and processed for SDS-PAGE. Sections of fluorograms are shown. C, whole cell extracts from mock infected (U) and PR8-infected MDCK cells treated with TIZ (+) or vehicle (−) were incubated with (+) or without (−) the cross-linking reagent ethylene glycol bis(succinimidylsuccinate) (EGS, 0.2 mm) and processed for Western blot using anti-HA antibodies. HA monomers (mark 1), dimers (mark 2), and trimers (mark 3) are indicated. A–C, slower- and faster-migrating HA0 forms in untreated or TIZ-treated cells are identified by asterisks and black arrowheads, respectively. D, immunofluorescence of mock infected (U) and WSN-infected A549 cells treated with TIZ (5 μg/ml) or vehicle for 24 h, labeled with anti-p230 trans-Golgi (red) and anti-HA (green) antibodies. The nuclei are stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue). The overlay of the three fluorochromes is shown (merge). The enlarged areas (insets) highlight the localization of HA in untreated and TIZ-treated cells. The images were captured and deconvolved with a DeltaVision microscope using SoftWoRx-2.50 software. Bar, 5 μm.