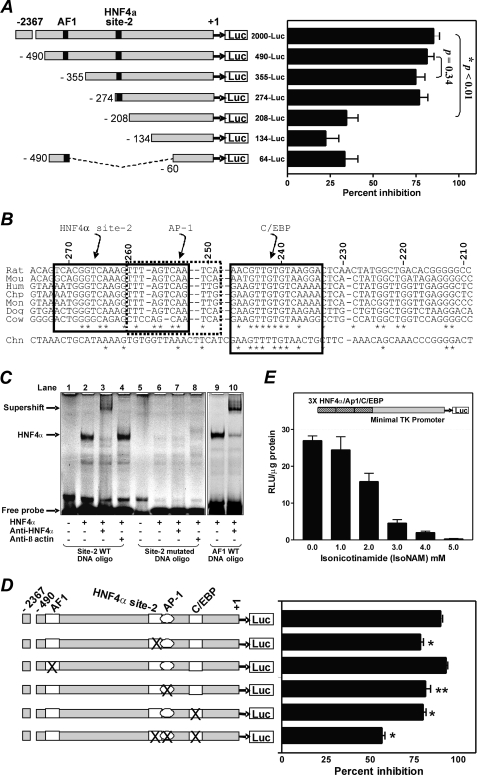
FIGURE 2.
A novel HNF4α binding site in the PEPCK-C gene promoter is required for IsoNAM-induced transcriptional repression. Panel A, HepG2 cells were treated with 5 mm IsoNAM or water (untreated control) after co-transfection of PKAc DNA and luciferase reporter constructs, which harbored various segments of the PEPCK-C gene promoter from rat. IsoNAM-dependent repression of transcription from the PEPCK-C gene promoter was expressed as a percent inhibition of treated as compared with untreated cells. Values were expressed as mean ± S.E. of four separate tests, with each test performed in triplicate. Panel B, the sequence from −272 to −208 of the rat PEPCK-C gene promoter was aligned with corresponding sequences from the mouse (Mou), human (Hum), chimpanzee (Chp), monkey (Mon), dog (Dog), cow (Cow), and chicken (Chn). Evolutionary conserved sites are indicated by boxes. Panel C, HNF4α binding site-2 interacted with HNF4α. Purified FLAG-HNF4α was used to perform an EMSA with the wild type or mutated DNA oligonucleotides corresponding to the HNF4α binding site-2 sequence, or with the wild type DNA corresponding to AF1, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” For the supershift assays, either anti-HNF4α serum or anti-β-actin serum was added to the reactions. Panel D, HNF4α binding sites were mutated individually or jointly with other conserved binding sites for AP1 and C/EBP in the p2000-Luc plasmid. The effect of IsoNAM on transcription from the PEPCK-C gene promoter, in the presence of co-transfected PKAc was measured using the procedure described under panel A. Values were expressed as mean ± S.E. of three separated tests, with each test done in triplicate. *, p < 0.001, and **, p < 0.016 as compared with the wild type gene promoter control. Panel E, an artificial promoter, composed of three copies of HNF4α-AP1-C/EBP binding sequences (−277/−218) and the TK minimal gene promoter, was cloned into pGL3-Basic vector to generate a reporter plasmid (inset). When this reporter plasmid was co-transfected with PKAc into HepG2 cells, IsoNAM caused a dose-dependent inhibition of transcription from the PEPCK-C gene promoter. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E. of three separate analyses.