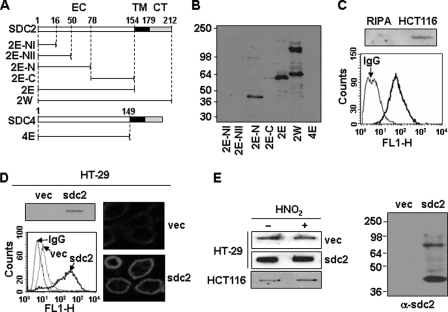
FIGURE 1.
Characterization of monoclonal antibody against syndecan-2. A, schematic representation of GST-syndecan-2 and -4 core proteins. The extracellular domain is represented by the white box (EC), the transmembrane domain by the black box (TM), and the cytoplasmic domain by the gray box (CT). Syndecan-2 and -4 are labeled with the amino acid number to show the location of deletion mutants. Shown are the whole extracellular domain of syndecan-2 (2E) and each deletion mutant (2E-NI (amino acids 1–16), 2E-NII (amino acids 1–50), 2E-N (amino acids 1–78), and 2E-C (amino acids 78–154)). B, GST-syndecan-2 core proteins were expressed in E. coli. Purified recombinant proteins were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-syndecan-2 antibodies. C, total cell lysates from HCT116 colon carcinoma cells were analyzed by slot blotting with anti-syndecan-2 antibody (top panel). HCT116 cells were incubated with anti-syndecan-2 antibodies, and the cell surface expression levels of syndecan-2 were analyzed by flow cytometry. IgG was used as a control (bottom). D, total cell lysates from HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cells and HT-29 stably expressing syndecan-2 (HT-29-sdc2) were analyzed by slot blotting with anti-syndecan-2 antibody (left, top). Cells were incubated with anti-syndecan-2 antibody, and the cell surface expression levels of syndecan-2 were analyzed by flow cytometry. IgG was used as a control (left, bottom). Cells were incubated with anti-syndecan-2 antibody, stained with a Texas Red-conjugated secondary antibody, and photographed under confocal microscopy (right). E, partially purified proteoglycans from HT-29, HT-29-sdc2, and HCT116 cells were treated with nitrous acid (HNO2) to degrade glycosaminoglycan chains. Syndecan-2 was analyzed by either slot blotting (left) or Western blotting (right) with anti-syndecan-2 antibody. Note that the proteins were recognized by the syndecan-2 antibody even after degradation of glycosaminoglycan chains with nitrous acid.