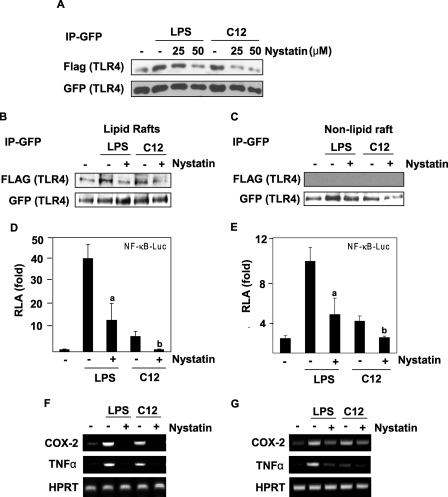
FIGURE 5.
Lipid raft inhibitor nystatin inhibits LPS- or lauric acid-induced homodimerization of TLR4, and the activation of NF-κB and TLR4 target gene expression. A, Ba/F3 cells were treated with nystatin prior to treatment with LPS or lauric acid for 30 min. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies and then immunoblotted with anti-FLAG antibodies. B, Ba/F3 cells were treated as in A but were lysed and fractionated by the sucrose gradient. GFP-TLR4 was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies from lipid raft fractions and immunoblotted with anti-FLAG antibodies. C, samples from the non-lipid raft fractions were immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted as in B. For the analysis of NF-κB-luciferase activity, Ba/F3-TLR4 cells (D) or RAW264.7 cells (E) transfected with NF-κB-luciferase construct were treated with nystatin for 8 h before the treatment with LPS or lauric acid. Cells were lysed to determine the luciferase activity. a and b were significantly different from the values for the control group without nystatin treatment. For the analysis of mRNA of indicated genes, Ba/F3-TLR4 cells (F) or RAW264.7 cells (G) were treated with nystatin for 6 h before treatment with LPS or lauric acid. RNAs were prepared and reverse transcription-PCR was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.”