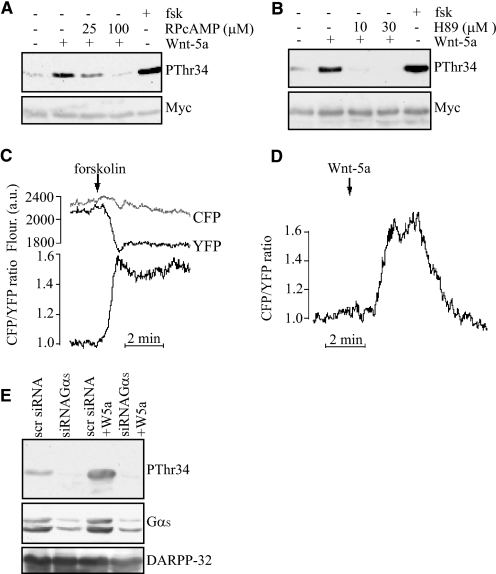
FIGURE 2.
Wnt-5a-induced Thr-34 phosphorylation of DARPP-32 involves cAMP elevation and activation of PKA. A, Western blot showing that the PKA inhibitor RPcAMPS inhibits rWnt-5a-induced Thr-34-DARPP-32 phosphorylation in DARPP-32-expressing MCF-7 cells, as detected by anti-pThr34 antibody. RPcAMPS was added in serum-free medium 1 h prior to stimulation with 0.4 μg/ml rWnt-5a for 5 min. Stimulation with 1 μm forskolin for 20 min was used as a positive control. B, Western blot showing H89 inhibition of rWnt-5a-induced pThr34-DARPP-32 phosphorylation in Myc-DARPP-32-expressing MCF-7 cells, as detected by anti-pThr34 antibody. H89 was added in serum-free medium 1 h prior to stimulation with 0.4 μg/ml rWnt-5a for 5 min. Stimulation with 1 μm forskolin for 20 min was used as a positive control. C and D, evanescent wave microscopy recording of CFP and YFP fluorescence and the cAMP-dependent CFP/YFP ratio from individual MCF-7 cells expressing a fluorescent cAMP biosensor. The cells are stimulated with 10 μm forskolin (C, n = 8) or 0.4 μg/ml Wnt-5a (D, n = 12) and the prestimulatory CFP/YFP ratio was normalized to unity. E, Thr-34-DARPP-32 phosphorylation after 5 min of stimulation with 0.4 μg/ml rWnt-5a in cells treated with siRNA targeting the Gαs protein or a scrambled sequence as a control. All of the Western blots shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.