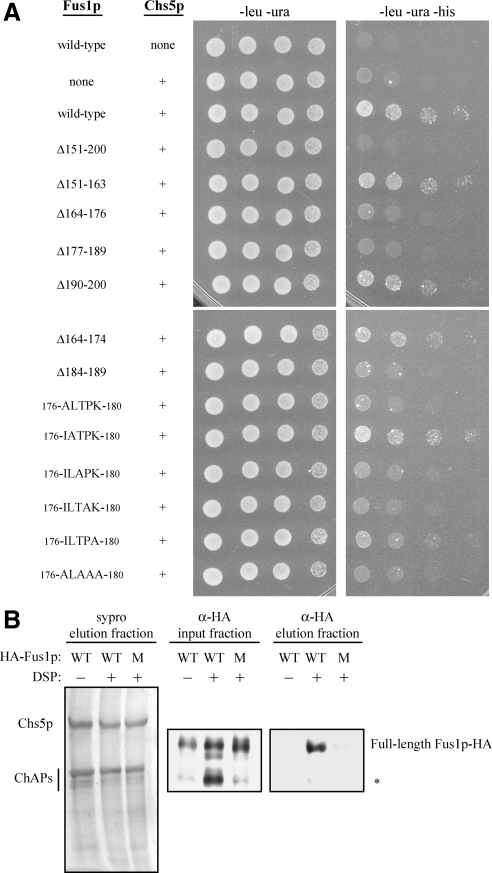
Figure 5.
Fus1p 176IXTPK180 is necessary for the physical interaction between Fus1p and Chs5p. (A) Yeast two-hybrid. Wild-type Fus1p (97-512) or a version of Fus1p (97-512) containing a small deletion or a mutation(s) in the 176ILTPK180 region was fused to the C terminus of the GAL4 activation domain (LEU). Chs5p (1-264) was fused to the C terminus of the GAL4 binding domain (URA). −leu −ura plates measure growth, whereas −leu −ura −his plates measure binding of the GAL4 activation domain to the GAL4 binding domain. (B) In vivo cross-linking and coimmunoprecipitation of Chs5p-TAP and Fus1p. Chromosomally TAP-tagged Chs5p was purified from cells expressing either wild-type (WT) or a 176ILTPK180 to 176ALAAA180 mutant (M) version of pMET25-FUS1-HA in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 5 mM DSP cross-linker. Purified Chs5p, which copurifies with all four ChAPs, was visualized in the final elution fraction with sypro staining. Fus1p-HA was visualized in input and final elution fractions by immunoblot analysis using an anti-HA antibody (diluted 1:1000; HA.11, Covance Research Products, Princeton, NJ). Fus1p-HA WT without DSP and Fus1p-HA mutant with DSP were purified 15 and 29% as well as Fus1p-HA WT with DSP, respectively, when factoring Fus1p-HA in the input fraction and purified Chs5p in the final elution fraction. Asterisk (*) indicates endogenously cleaved Fus1p-HA species (see text for details).