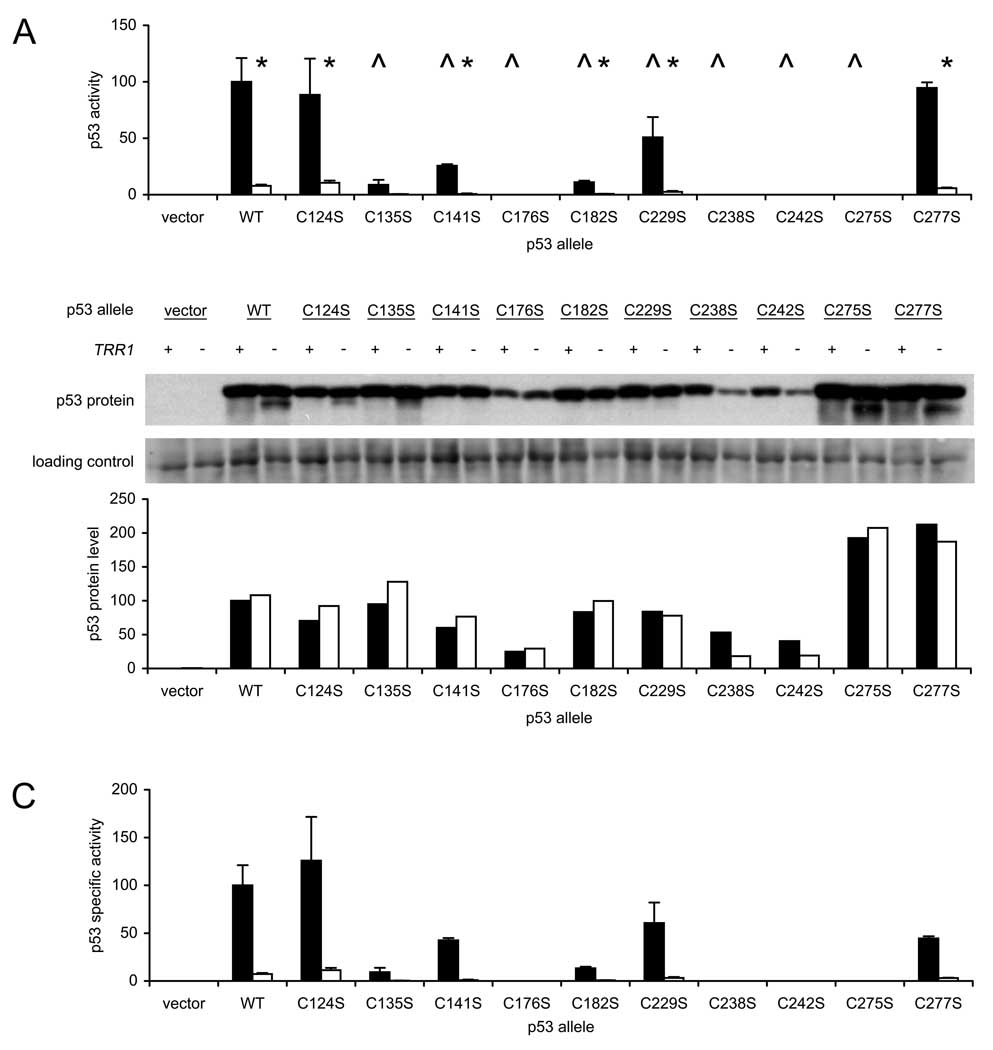
Figure 6.
Activity and thioredoxin reductase-dependence of p53 alleles carrying single Cys-to-Ser mutations. A. Wild-type (TRR1, dark bars) and thioredoxin-null (Δtrr1, light bars) yeast carrying an integrated p53-dependent LacZ reporter gene were transformed with single-copy plasmids expressing the indicated p53 allele, and three independent transformants were assayed for β-galactosidase activity. Bars represent activity levels (mean ± S.D.), normalized to the level in wild-type yeast expressing native p53. Carat (^) indicates genotypes where activity of native and mutated p53 alleles differed significantly when expressed in wild-type yeast (p < 0.05, by t-test). Asterisk (*) indicates genotypes where p53 activity in wild-type and mutant yeast differed significantly (p < 0.05, by t-test). B. Immunoblot analysis of p53 protein levels in yeast transformed with mutated p53 alleles and specific activity of each protein in transactivating reporter gene expression. Equal amounts of lysate protein (20 µg) from representative transformants was resolved by SDS-PAGE, and p53 protein was detected by immunoblotting using DO-1 antibody (upper panel). An 80-kDa protein, detected by SYPRO Ruby staining prior to immunostaining, was used as a loading control (center panel). The relative amount of p53 protein in each sample was calculated by dividing the p53 band intensity by the 80-kDa protein band intensity, and dividing the resulting ratio by the ratio observed in wild-type yeast expressing native p53. TRR1, dark bars; Δtrr1, light bars (lower panel). C. The specific activity of p53 in stimulating reporter gene expression was calculated by dividing the β-galactosidase levels shown in Figure 6A by the p53 protein levels determined in Figure 6B. Bars represent mean ± S.D. for three transformants.