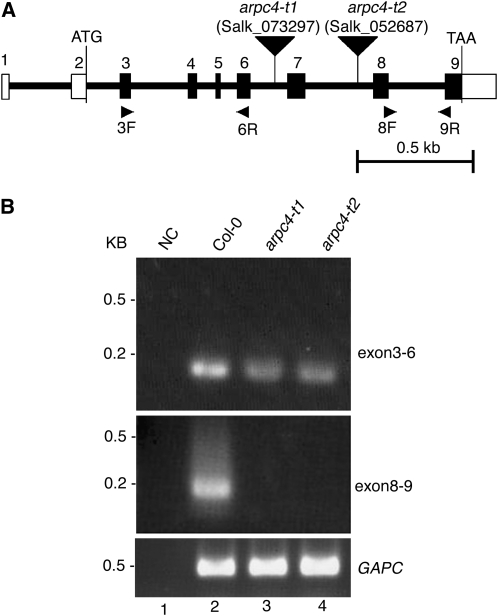
Figure 1.
Physical map of the ARPC4 gene and characterization of the arpc4 T-DNA insertion alleles. A, The positions of exons (numbered vertical rectangles) and introns (thick lines) are represented. The start and stop codons are indicated, and the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions are labeled with open rectangles. The locations of the arpc4-t1 and arpc4-t2 T-DNA insertions are shown using inverted black triangles. The names and locations of primers used for RT-PCR experiments are also indicated. Bar = 0. 5 kb. B, The T-DNA insertions cause premature transcriptional termination. Transcription of the ARPC4 exons upstream (top panel; using primers 3F and 6R) and downstream (middle panel; using primers 8F and 9R) from the T-DNA was monitored. The quality of the RNA was assayed using primers to detect glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase subunit C (GAPC; bottom panel). NC is a “no-template” control for the potential contamination of reagents with ARPC4 cDNA. DNA size standards are shown to the left.