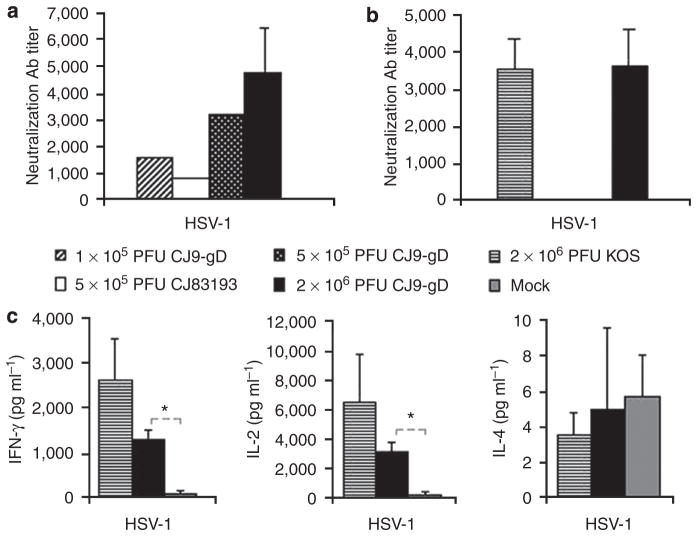
Figure 1. Induction of herpes simplex virus (HSV)-1-specific neutralizing antibodies (Abs) and T-cell responses in immunized mice.
(a) Three sets of BALB/c mice (n = 6; n = 17; n = 17) were injected with 2 × 106 PFU per mouse of CJ9-gD or DMEM. Two sets of 32 BALB/c mice (eight mice per group) were mock-vaccinated with DMEM, or vaccinated with CJ9-gD or CJ83193 at the indicated doses. At 4 weeks after primary immunization, the blood was collected and pooled for each group, and HSV-1-specific neutralizing Ab titers were determined. The results represent average titers ± SEM. (b) BALB/c mice were mock-immunized with DMEM (n = 2) or immunized with either KOS (n = 5) or CJ9-gD (n = 4) at 2 × 106 PFU per mouse. AT 6 months after the primary immunization, blood and splenocytes were collected individually from each mouse. Serum was assayed for HSV-1-specific neutralizing Ab titers. (c) Splenocytes from mice described in (b) were cultured in the presence or absence of UV-inactivated HSV-1 strain McKrae. Levels of IFN-γ, IL-2, and IL-4 in supernatants were determined by ELISA. The results represent average cytokine levels after subtraction of background values from mock-stimulated wells ± SEM. P-values were assessed by student’s t-test (*P<0.05).