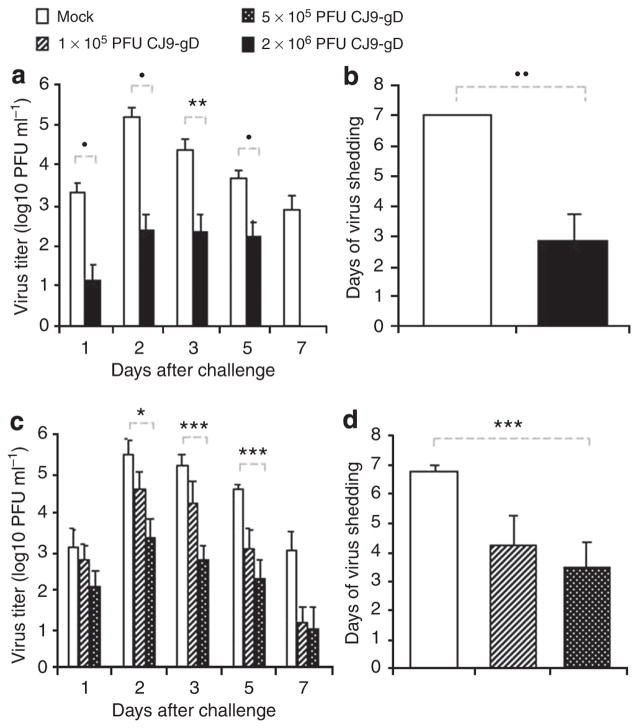
Figure 7. Reduction of challenge herpes simplex virus (HSV-2) vaginal replication in mice immunized with CJ9-gD.
One set of 17 female BALB/c mice were subcutaneously (s.c.) injected either with 2 × 106 PFU per mouse of CJ9-gD or with DMEM (a and b). One set of 24 female 6- to 8-week-old BALB/c mice was injected s.c. either with 1 × 105 PFU of CJ9-gD, 5 × 105 PFU of CJ9-gD, or with DMEM (c and d). Mice were boosted after 2 weeks. At 4 weeks, mice were pretreated with medroxyprogesterone and challenged intravaginally with 1 × 105 PFU of HSV-2 strain 186. Vaginal swabs were taken on days 1, 2, 3, 5, and 7 post-challenge. Infectious viruses in the swab materials were assessed by standard plaque assay on Vero cell monolayers. Viral titers are expressed as the mean ± SEM in the individual vaginal swabs (a and c). The duration of viral shedding is represented as the mean number of days during which injections virus was detected in swab material after challenge ± SEM (b and d). P was assessed by student’s t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, •P < 0.001, ••P < 0.0005).