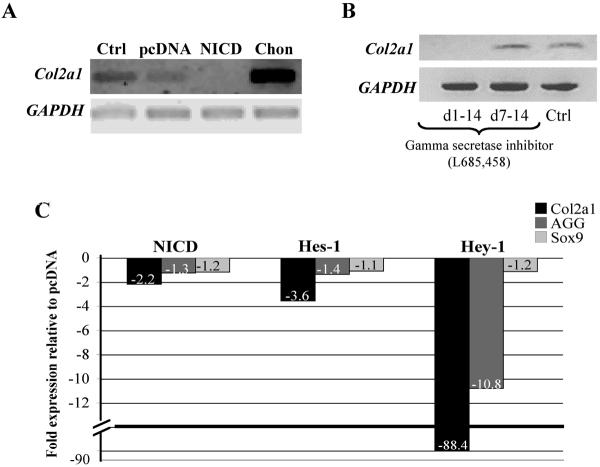
Figure 2. NICD, Hes-1 and Hey-1 over expression and timing of γ-SI inhibitor treatment prevents chondrogenic differentiation.
A constitutively active form of human Notch-1 construct or control pcDNA3.1 was transfected into monolayer cultured hMSC and then placed into pellet culture for 14 days. NICD over expression reduced Col2a1 expression levels (panel A). The gamma secretase inhibitor (γSI; L685–458) was either added to hMSC pellet cultures from days 1 to 14 or added on day 7 to day 14. Col2a1 expression was abolished in pellets treated for the entire culture period, but not for the second week, indicating that Notch signaling is essential in early chondrogenic differentiation (panel B). NICD, Hes-1 and Hey-1 plasmids were transfected into human MSC and maintained in pellet culture for 6 days. In comparison to pcDNA transfected pellets, NICD, Hes-1 and especially Hey-1 overexpression led to a repression of Col2a1 gene expression levels (panel B). Hey-1 over expression reduced aggrecan (AGG) expression while NICD and Hes-1 did not. Sox9 expression was not altered by these treatments (panel C). Ctrl: Mock nucleofection without plasmid. Chon: Chondrocyte positive control.