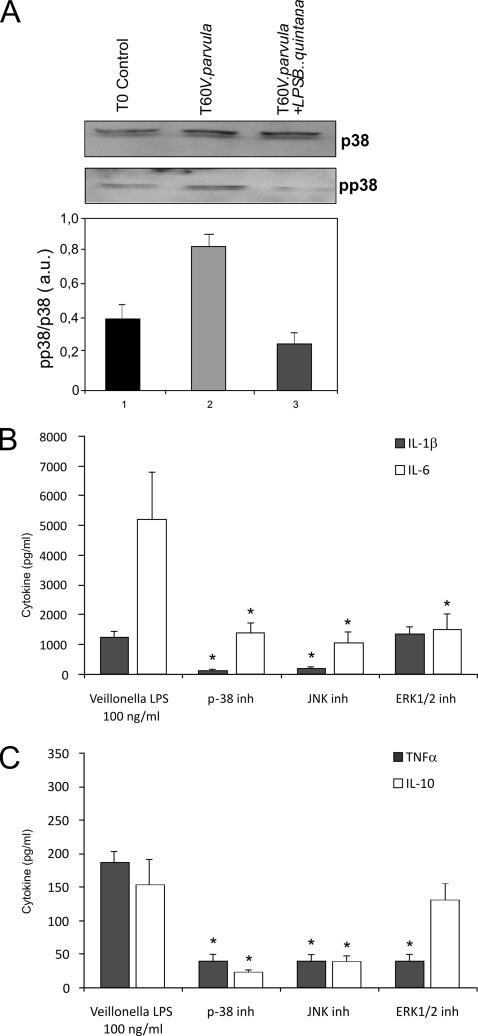
FIG. 5.
Veillonella LPS activates p38 MAPK. (A) Effects of TLR4 inhibition by B. quintana LPS on Veillonella LPS-stimulated p38 activation in human PBMC. Protein extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and analyzed by Western blotting using specific anti-p38 and anti-phopsho-p38 antibodies. The intensity of phospho-p38-specific bands was measured by densitometry and is reported as arbitrary units (a.u.) of phosho-p38 expression after normalization with p38 levels. The means ± standard errors of the means of three independent experiments are shown. (B and C) Effects of pharmacological inhibition of p38 MAPK-, JNK-, and ERK-mediated pathways during Veillonella LPS stimulation of PBMC; the graphs show IL-1β and IL-6 production after inhibition of p38 MAPK, JNK, and ERK (B) or TNF-α and IL-19 production (C). Data represent the means ± standard deviations for cytokine production of at least four healthy volunteers. Note the strong suppression of cytokine production after inhibition of p38 MAPK and JNK. *, P < 0.01 (Wilcoxon rank test).