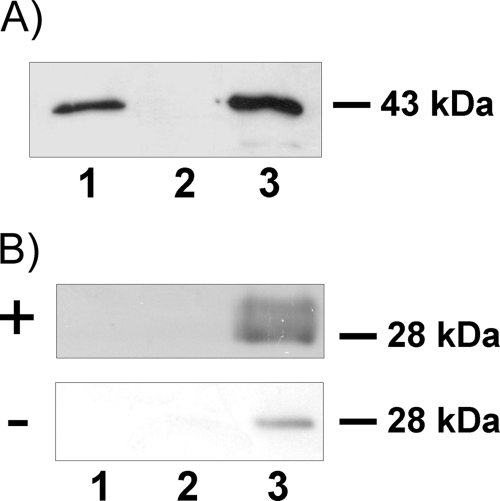
FIG. 5.
Interaction between EmABP and human apoA-I. (A) Interaction of purified EmABP and apoA-I. Purified, recombinant apoA-I was bound to protein G-agarose beads using the anti-apoA-I antibody. The recombinantly expressed, purified thio-EmABP fusion protein was added, and after 2 h of incubation, agarose G beads were pelleted and thoroughly washed. The protein complexes were then separated on a 12% acrylamide gel, and Western blot detection using the anti-V5 antibody (Invitrogen) was carried out. In lane 1, the anti-apoA-I antibody, apoA-I, and thio-EmABP were applied. Conditions in lane 2 were identical to lane 1 except that apoA-I was omitted. In lane 3, the original input of thio-EmABP is shown. (B) Precipitation of apoA-I from human serum. The anti-V5 antibody was bound to Sepharose A beads (lanes 1 to 3), followed by the addition of the thio-EmABP fusion protein (lane 3) or the thio-V5-His6 control protein (lane 2) (in lane 1, no fusion protein was added). The antibody protein complexes were incubated overnight with serum from AE patients (+) or healthy donors (−). The Sepharose A beads were then pelleted and thoroughly washed. Protein complexes were separated on an 12% acrylamide gel, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and detected using an anti-apoA-I antibody.