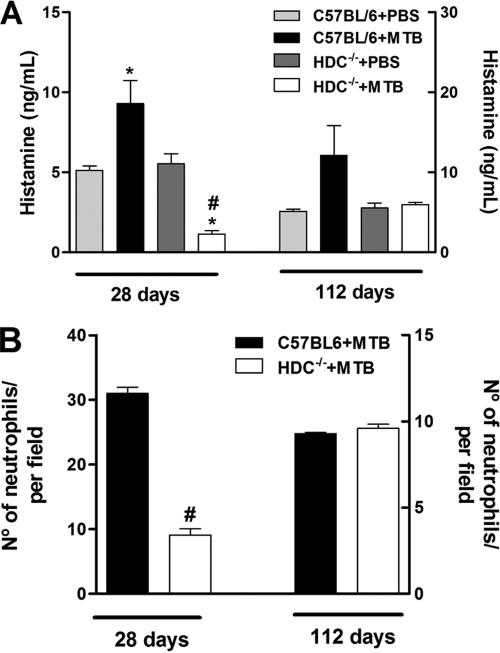
FIG. 1.
HDC−/− mice displayed marked histamine inhibition and decreased neutrophil number in response to M. tuberculosis infection. (A) C57BL/6 and HDC−/− mice were infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv (1 × 102 bacilli/mouse) by an intranasal route (black and white bars, respectively) or not infected (light gray and dark gray bars, respectively). Histamine concentrations were measured in lung tissue from uninfected and infected C57BL/6 or HDC−/− mice at the same time points. (B) Quantification of neutrophils in lung tissue from C57BL/6 or HDC−/− (black and white bars, respectively) mice after 28 and 112 days of infection. The results are expressed as means ± SEM from at least five animals in experiments repeated twice. Statistical testing found a significant difference (P < 0.05) relative to uninfected (*) or M. tuberculosis-infected (#) C57BL/6 mice. Statistical variations were analyzed by ANOVA followed by Tukey posttest. PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.