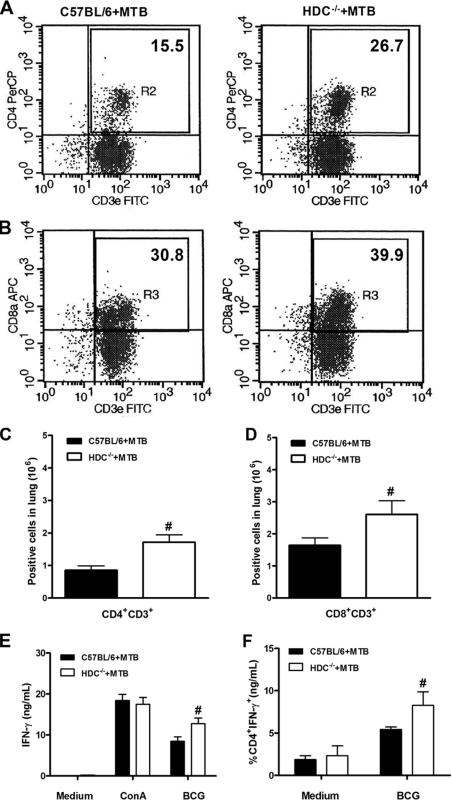
FIG. 5.
HDC−/− mice showed an augmented CD4+ T-cell influx in the lungs upon M. tuberculosis infection. Lung tissue was removed at 28 days after M. tuberculosis H37Rv infection (102 CFU intranasally) and lung cells from M. tuberculosis-infected C57BL/6 (black bars in panels C to F) or HDC−/− (white bars in panels C to F) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry for the percentage of CD4+ CD3+ (A) and CD8+ CD3+ (B) T cells. Results are expressed as the absolute number of positive cells per lung (C and D). Further, isolated lung cells were restimulated with BCG or ConA for 48 h, and IFN-γ production was assessed in supernatant by ELISA (E) and in T cells stained for intracellular IFN-γ as a percentage of CD4 T cells expressing IFN-γ (F). Means ± SEM from at least five mice per group in one independent experiment repeated twice are shown. Numeral signs represent a significant difference (P < 0.05) relative to M. tuberculosis-infected C57BL/6 mice. Statistical variations were analyzed by Student's t test. PerCP, peridinin chlorophyll protein.